前言
有些小伙伴在工作中可能遇到过这样的场景:原本运行良好的Group By查询,随着数据量的增长,执行时间从几秒变成了几分钟甚至几小时。
页面加载缓慢,用户抱怨连连,DBA着急上火。
这种性能下降往往是在不知不觉中发生的,背后一定有着深层次的原因。
今天这篇文章跟大家一起聊聊group by变慢后,如何定位和优化,希望对你会有所帮助。
一、为什么Group By会变慢?
在深入解决方案之前,我们需要先理解Group By操作的本质。
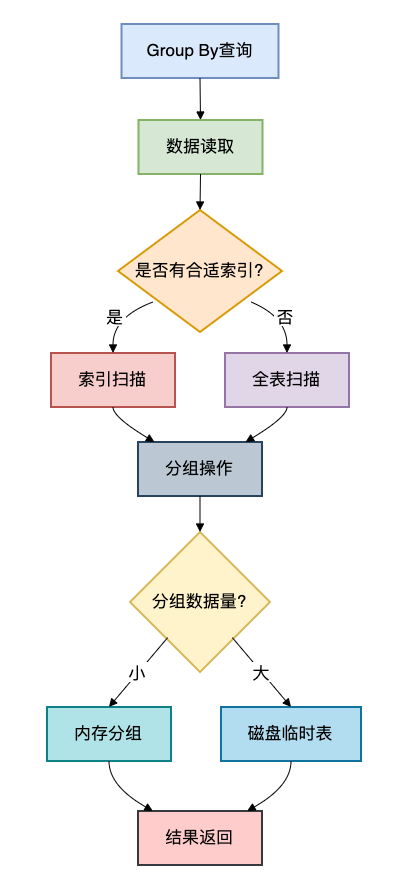
Group By的执行过程通常包含以下几个步骤:
 图片
图片
从流程图可以看出,Group By性能问题主要出现在两个环节:数据读取和分组操作。
数据读取阶段可能因为没有索引而全表扫描,分组操作阶段可能因为数据量过大而使用磁盘临时表。
这两个问题都会导致group by性能变慢。
二、如何定位Group By性能问题?
1. 使用EXPLAIN分析执行计划
MySQL的EXPLAIN命令是我们分析查询性能的首选工具:
复制
EXPLAIN
SELECT department, COUNT(*) as emp_count
FROM employees
WHERE hire_date > 2020-01-01
GROUP BY department;1.2.3.4.5.
执行结果可能包含以下关键信息:
列名
说明
可能的值和含义
type
访问类型
index(索引扫描), ALL(全表扫描)
key
使用的索引
实际使用的索引名称
rows
预估扫描行数
数值越小越好
Extra
额外信息
Using temporary(使用临时表), Using filesort(使用文件排序)
2. 性能监控工具
除了EXPLAIN,我们还可以使用MySQL的性能监控工具:
复制
-- 开启性能分析
SET PROFILING = 1;
-- 执行查询
SELECT department, COUNT(*) as emp_count
FROM employees
GROUPBY department;
-- 查看性能详情
SHOW PROFILE FORQUERY1;
-- 查看所有查询的性能信息
SHOWPROFILES;1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.
三、常见原因及解决方案
1. 缺少合适的索引
问题分析: 有些小伙伴在设计表结构时,可能没有为Group By字段和Where条件字段创建合适的索引,导致MySQL不得不进行全表扫描。
解决方案: 为Group By字段和Where条件字段创建复合索引:
复制
-- 创建适合Group By的索引
CREATE INDEX idx_department_hire_date ON employees(department, hire_date);
-- 或者创建覆盖索引,避免回表操作
CREATE INDEX idx_department_hire_date_covering ON employees(department, hire_date, salary);1.2.3.4.5.
索引设计原则:
将Where条件中的字段放在索引左侧然后是Group By字段最后是Select中需要返回的字段(覆盖索引)
2. 使用临时表和文件排序
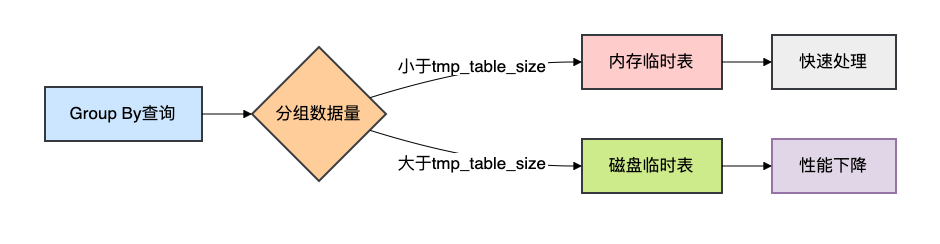
问题分析: 当Group By的数据量较大时,MySQL可能需要使用临时表来存储中间结果,如果临时表太大而内存放不下,就会使用磁盘临时表,性能急剧下降。
 图片
图片
解决方案:
方法一:调整临时表大小
复制
-- 查看当前临时表设置
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE tmp_table_size;
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE max_heap_table_size;
-- 增大临时表内存大小(需重启)
SET GLOBAL tmp_table_size = 256 * 1024 * 1024; -- 256MB
SET GLOBAL max_heap_table_size = 256 * 1024 * 1024; -- 256MB1.2.3.4.5.6.7.
方法二:优化查询语句
复制
-- 优化前:查询所有字段
SELECT *, COUNT(*)
FROM employees
GROUPBY department;
-- 优化后:只查询需要的字段
SELECT department, COUNT(*)
FROM employees
GROUPBY department;
-- 进一步优化:添加限制条件减少处理数据量
SELECT department, COUNT(*)
FROM employees
WHERE hire_date > 2023-01-01
GROUPBY department;1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.
3. 数据量过大问题
问题分析: 当单表数据量达到千万级甚至亿级时,即使有索引,Group By操作也可能很慢。
解决方案:
方法一:分阶段聚合
复制
// Java代码示例:分阶段聚合大量数据
public Map<String, Integer> batchGroupBy(String tableName,
String groupColumn,
String condition,
int batchSize) throws SQLException {
Map<String, Integer> resultMap = new HashMap<>();
int offset = 0;
boolean hasMore = true;
try (Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection()) {
while (hasMore) {
String sql = String.format(
"SELECT %s, COUNT(*) as cnt FROM %s WHERE %s GROUP BY %s LIMIT %d OFFSET %d",
groupColumn, tableName, condition, groupColumn, batchSize, offset);
try (Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql)) {
int rowCount = 0;
while (rs.next()) {
String key = rs.getString(groupColumn);
int count = rs.getInt("cnt");
resultMap.merge(key, count, Integer::sum);
rowCount++;
}
if (rowCount < batchSize) {
hasMore = false;
} else {
offset += batchSize;
}
}
}
}
return resultMap;
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.
方法二:使用异步处理和缓存
复制
// 异步Group By处理示例
@Service
publicclass AsyncGroupByService {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
private CacheManager cacheManager;
@Async("taskExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<Map<String, Integer>> executeGroupByAsync(String sql, String cacheKey) {
// 检查缓存
Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache("groupByResults");
Cache.ValueWrapper cachedResult = cache.get(cacheKey);
if (cachedResult != null) {
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture((Map<String, Integer>) cachedResult.get());
}
// 执行查询
Map<String, Integer> result = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, rs -> {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
while (rs.next()) {
map.put(rs.getString(1), rs.getInt(2));
}
return map;
});
// 设置缓存
cache.put(cacheKey, result);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(result);
}
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.
4. 复杂Group By优化
问题分析: 有些小伙伴可能会写出包含多个字段、复杂条件甚至包含子查询的Group By语句,这些语句往往性能较差。
解决方案:
方法一:使用派生表优化
复制
-- 优化前:复杂Group By
SELECT department,
AVG(salary) as avg_salary,
COUNT(*) as emp_count
FROM employees
WHERE hire_date > 2020-01-01
GROUPBY department
HAVING avg_salary > 5000;
-- 优化后:使用派生表
SELECT t.department, t.avg_salary, t.emp_count
FROM (
SELECT department,
AVG(salary) as avg_salary,
COUNT(*) as emp_count
FROM employees
WHERE hire_date > 2020-01-01
GROUPBY department
) t
WHERE t.avg_salary > 5000;1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.
方法二:使用WITH ROLLUP进行多维度分组
复制
-- 多层次分组统计
SELECT department, job_title, COUNT(*) as emp_count
FROM employees
GROUP BY department, job_title WITH ROLLUP;
-- 等价于以下三个查询的联合
-- 1. GROUP BY department, job_title
-- 2. GROUP BY department
-- 3. 总计1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.
5. 分布式环境下的Group By优化
问题分析: 在分库分表环境下,Group By操作变得更加复杂,需要在多个节点上执行并合并结果。
解决方案:
方法一:使用中间件实现跨库Group By
复制
// 分库分表Group By处理示例
publicclass ShardingGroupByExecutor {
public Map<String, Integer> executeAcrossShards(String logicSql, List<DataSource> shards) {
// 并发执行所有分片
List<CompletableFuture<Map<String, Integer>>> futures = shards.stream()
.map(shard -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> executeOnShard(logicSql, shard)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 合并所有结果
return futures.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.flatMap(map -> map.entrySet().stream())
.collect(Collectors.toMap(
Map.Entry::getKey,
Map.Entry::getValue,
Integer::sum
));
}
private Map<String, Integer> executeOnShard(String sql, DataSource dataSource) {
try (Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql)) {
Map<String, Integer> result = new HashMap<>();
while (rs.next()) {
result.put(rs.getString(1), rs.getInt(2));
}
return result;
} catch (SQLException e) {
thrownew RuntimeException("分片查询失败", e);
}
}
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.
方法二:使用Elasticsearch等搜索引擎
对于复杂的聚合查询,可以考虑将数据同步到Elasticsearch中,利用其强大的聚合能力:
复制
// Elasticsearch聚合查询示例
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("employees");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
// 构建聚合
TermsAggregationBuilder aggregation = AggregationBuilders.terms("by_department")
.field("department.keyword")
.subAggregation(AggregationBuilders.avg("avg_salary").field("salary"));
sourceBuilder.aggregation(aggregation);
searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);
// 执行查询
SearchResponse response = client.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 处理结果
Terms terms = response.getAggregations().get("by_department");
for (Terms.Bucket bucket : terms.getBuckets()) {
String department = bucket.getKeyAsString();
long count = bucket.getDocCount();
Avg avgSalary = bucket.getAggregations().get("avg_salary");
System.out.println(department + ": " + count + ", 平均薪资: " + avgSalary.getValue());
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.
四、实战案例
有些小伙伴在电商系统中可能会遇到订单统计的Group By性能问题,下面是一个真实案例:
原始查询:
复制
SELECT DATE(create_time) as order_date,
product_category,
COUNT(*) as order_count,
SUM(amount) as total_amount
FROM orders
WHERE create_time >= 2023-01-01
AND status = COMPLETED
GROUP BY DATE(create_time), product_category;1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.
优化方案:
创建合适索引:
复制
CREATE INDEX idx_orders_stats ON orders(create_time, status, product_category, amount);1.
使用预聚合:
复制
-- 创建预聚合表
CREATETABLE orders_daily_stats (
stat_date DATENOTNULL,
product_category VARCHAR(50) NOTNULL,
order_count INTNOTNULL,
total_amount DECIMAL(15,2) NOTNULL,
PRIMARY KEY (stat_date, product_category)
);
-- 使用定时任务每天凌晨更新统计
INSERTINTO orders_daily_stats
SELECTDATE(create_time), product_category, COUNT(*), SUM(amount)
FROM orders
WHERE create_time >= CURDATE() - INTERVAL1DAY
ANDstatus = COMPLETED
GROUPBYDATE(create_time), product_category
ONDUPLICATEKEYUPDATE
order_count = VALUES(order_count),
total_amount = VALUES(total_amount);1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.
查询优化后的结果:
复制
-- 现在查询预聚合表,性能极大提升
SELECT stat_date, product_category, order_count, total_amount
FROM orders_daily_stats
WHERE stat_date >= 2023-01-01;1.2.3.4.
总结
通过以上分析和解决方案,我们可以总结出Group By性能优化的关键点:
索引优化:为Group By字段和Where条件创建合适的复合索引查询简化:避免SELECT *,只获取需要的字段临时表优化:调整tmp_table_size,避免磁盘临时表数据分片:对于大数据集,采用分批次处理策略预聚合:对于常用统计,使用预聚合表提前计算架构升级:考虑使用读写分离、分布式数据库或搜索引擎
不同场景下的优化策略选择:
场景
推荐策略
优点
缺点
中小数据量
索引优化+查询优化
简单有效
需要设计合适的索引
大数据量
预聚合+分批次处理
性能提升明显
需要额外存储空间
高并发查询
缓存+异步处理
降低数据库压力
数据可能不是实时
复杂聚合
使用Elasticsearch
聚合能力强
需要数据同步
Group By性能优化是一个需要综合考虑数据库设计、查询编写和系统架构的系统工程。
每个业务场景都有其特殊性,需要根据实际情况选择合适的优化方案。
 图片
图片 图片
图片