在操作系统的庞大体系中,Linux 内存管理堪称基石般的存在,它如同一位幕后的大管家,精心调度着系统中宝贵的内存资源。从进程的创建到运行,再到结束,内存管理贯穿始终,确保每个进程都能获得所需的内存空间,同时避免内存的浪费与冲突。它不仅为进程提供了独立的地址空间,保障了进程间的隔离与安全,还通过一系列复杂而精妙的机制,实现了物理内存的高效利用,让系统在有限的内存条件下也能稳定且高效地运行。
而页面回收技术,作为 Linux 内存管理中的关键一环,更是扮演着不可或缺的角色。当系统内存资源紧张时,页面回收技术就如同一位救火队员,迅速行动起来,将那些不再被频繁使用的页面从内存中回收,释放出宝贵的内存空间,以供其他更急需内存的进程使用。它的存在,有效避免了系统因内存不足而陷入崩溃的困境,保障了系统的持续稳定运行 。同时,页面回收技术也极大地提高了内存的利用率,使得系统能够在有限的内存资源下,承载更多的进程和任务,提升了系统的整体性能和效率。接下来,就让我们深入探索 Linux 内核页面回收技术的奥秘。
一、页面回收简介
1.1概述
随着linux系统不断分配内存,当系统内存压力越来越大时,就会对系统的每个压力大的zone进程内存回收,内存回收主要是针对匿名页和文件页进行的。对于匿名页,内存回收过程中会筛选出一些不经常使用的匿名页,将它们写入到swap分区中,然后作为空闲页框释放到伙伴系统。
而对于文件页,内存回收过程中也会筛选出一些不经常使用的文件页,如果此文件页中保存的内容与磁盘中文件对应内容一致,说明此文件页是一个干净的文件页,就不需要进行回写,直接将此页作为空闲页框释放到伙伴系统中,相反,如果文件页保存的数据与磁盘中文件对应的数据不一致,则认定此文件页为脏页,需要先将此文件页回写到磁盘中对应数据所在位置上,然后再将此页作为空闲页框释放到伙伴系统中。这样当内存回收完成后,系统空闲的页框数量就会增加,能够缓解内存压力。
要说清楚内存的页面回收,就必须要先理清楚内存分配过程,当我们申请分配页的时候,页分配器首先尝试使用低水线分配页,如果成功,就是走快速路径;如果失败,就是走慢速路径,说明内存轻微不足,页分配器将会唤醒内存节点的页回收内核线程,异步回收页。然后尝试使用最低水线分配页。如果使用最低水线分配失败,走最慢的路径,说明内存严重不足,页分配器会直接回收。针对不同的物理页,采用不同的回收策略:交换支持的页和存储设备支持的文件页。
在发现内存紧张时,也就是慢路径上,系统就会通过一系列机制来回收内存,比如下面这三种方式:
回收缓存,比如使用 LRU(Least Recently Used)算法,回收最近使用最少的内存页面;Linux内核使用LRU(Least Recently Used,最近最少使用)算法选择最近最少使用的物理页。回收物理页的时候,如果物理页被映射到进程的虚拟地址空间,那么需要从页表中删除虚拟页到物理页的映射。回收不常访问的内存,把不常用的内存通过交换分区直接写到磁盘中;回收不常访问的内存时,会用到交换分区(以下简称 Swap)。Swap 其实就是把一块磁盘空间当成内存来用。它可以把进程暂时不用的数据存储到磁盘中(这个过程称为换出),当进程访问这些内存时,再从磁盘读取这些数据到内存中(这个过程称为换入)。杀死进程,内存紧张时系统还会通过 OOM(Out of Memory),直接杀掉占用大量内存的进程。
OOM(Out of Memory)其实是内核的一种保护机制。它监控进程的内存使用情况,并且使用 oom_score 为每个进程的内存使用情况进行评分,一个进程消耗的内存越大,oom_score 就越大;一个进程运行占用的 CPU 越多,oom_score 就越小。这样,进程的 oom_score 越大,代表消耗的内存越多,也就越容易被 OOM 杀死,从而可以更好保护系统。
回收缓存和回收不常访问的内存一般都是使用LRU算法选择最近最少使用的物理页。
选择目标页
PFRA的目标就是获得页框并使之空闲。PFRA按照页框所含内容,以不同的方式处理页框。我们将他们区分成:不可回收页、可交换页、可同步页和可丢弃页:
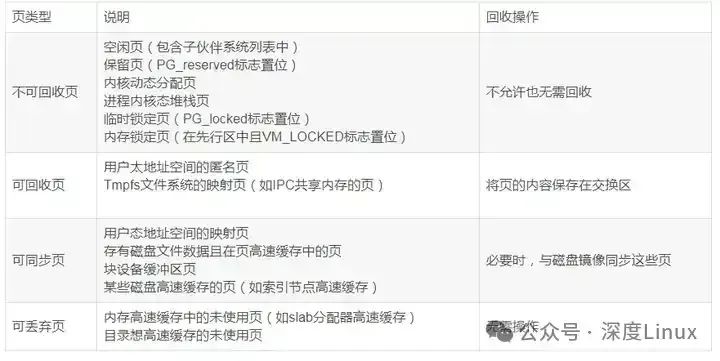 图片
图片
进行页面回收的时机
Linux操作系统使用如下这两种机制检查系统内存的使用情况,从而确定可用的内存是否太少从而需要进行页面回收。
周期性的检查:这是由后台运行的守护进程 kswapd 完成的。该进程定期检查当前系统的内存使用情况,当发现系统内空闲的物理页面数目少于特定的阈值时,该进程就会发起页面回收的操作。
“内存严重不足”事件的触发:在某些情况下,比如,操作系统忽然需要通过伙伴系统为用户进程分配一大块内存,或者需要创建一个很大的缓冲区,而当时系统中的内存没有办法提供足够多的物理内存以满足这种内存请求,这时候,操作系统就必须尽快进行页面回收操作,以便释放出一些内存空间从而满足上述的内存请求。这种页面回收方式也被称作“直接页面回收”。
睡眠回收,在进入suspend-to-disk状态时,内核必须释放内存。
如果操作系统在进行了内存回收操作之后仍然无法回收到足够多的页面以满足上述内存要求,那么操作系统只有最后一个选择,那就是使用 OOM( out of memory )killer,它从系统中挑选一个最合适的进程杀死它,并释放该进程所占用的所有页面。
上面介绍的内存回收机制主要依赖于三个字段:pages_min,pages_low 以及 pages_high。每个内存区域( zone )都在其区域描述符中定义了这样三个字段,这三个字段的具体含义如下表 所示。
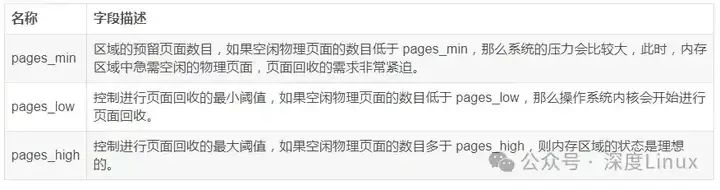
1.2为什么需要页面回收
在计算机系统中,内存是一种极其宝贵且有限的资源 ,就像我们生活中的房子,空间总是有限的。而进程对内存的需求却如同一个永远填不满的无底洞,随着各种应用程序的不断启动和运行,它们对内存的渴望也在持续攀升。当一个新的进程诞生时,它就会向系统申请内存空间,用于存储自身的代码、数据以及运行时产生的各种临时信息。随着进程的不断增加,内存资源会逐渐变得紧张起来 。
倘若没有页面回收机制,系统就好比一个只进不出的仓库,随着物品(进程数据)的不断堆积,迟早会出现内存耗尽的严重问题。一旦内存耗尽,新的进程将无法获得足够的内存来启动,正在运行的进程也可能因为缺乏内存而无法正常执行任务,导致系统响应变得迟缓,甚至完全瘫痪,就像一座交通拥堵到极致的城市,所有车辆都无法正常通行 。
页面回收技术的出现,就像是为这座拥堵的城市开辟了新的通道,它能够在系统内存紧张时,及时将那些不再被频繁使用的页面从内存中回收,释放出宝贵的内存空间,让内存资源能够得到更高效的利用。这不仅保证了系统的稳定运行,避免了因内存不足而引发的各种故障,还能让系统在有限的内存条件下,接纳更多的进程和任务,大大提升了系统的整体性能和效率 。所以,页面回收技术对于 Linux 系统来说,是维持其稳定与高效运行的关键所在。
二、页面回收技术原理剖析
2.1页面分类与标识
在 Linux 系统这个庞大的内存世界里,页面如同形态各异的居民,有着不同的类型。其中,匿名页和文件映射页是较为常见的两种类型。匿名页就像是无家可归的流浪汉,没有与任何磁盘文件建立关联,主要用于存储进程的堆和栈等动态分配的数据。想象一下,进程在运行过程中,需要临时存放一些数据,这些数据就如同旅客的随身物品,匿名页就是提供给这些物品存放的临时空间 。
而文件映射页则像是有固定住址的居民,它与磁盘文件紧密相连,通过内存映射机制,将文件的内容映射到内存中,使得进程可以直接访问文件数据,就像直接从自己家里拿东西一样方便 。
内核为了更好管理这些页面,就像社区管理员管理居民信息一样,使用了页描述符等数据结构。页描述符就像是居民的信息登记表,详细记录了页面的各种信息,如页面的状态、引用计数、映射信息等 。通过这些信息,内核能够快速了解每个页面的情况,判断页面是否被使用、是否可以回收等 。不同类型的页面在回收过程中也有着不同的待遇。对于匿名页来说,由于它没有对应的磁盘文件,当系统内存紧张时,它可能会被交换(换出)到交换分区中,就像把暂时不用的物品存放到仓库里,以腾出物理内存供其他进程使用 。
而文件映射页,如果它的内容没有被修改,那么在回收时可以直接释放,下次进程访问时再从磁盘读取,就像从仓库里重新取出物品;但如果内容被修改过,就需要先将修改后的内容写回磁盘,然后才能释放,这就像是在归还物品前,要先把物品整理好一样 。
2.2LRU 链表与老化机制
LRU 链表,即最近最少使用链表,在 Linux 内核页面回收技术中扮演着重要的角色,它就像是一个特殊的队列,按照页面的使用情况对页面进行排序。LRU 链表的工作原理基于一个简单而实用的假设:最近最少使用的页在较短的时间内也不太可能被频繁使用 。这就好比我们日常生活中,那些很久都没有用过的物品,在接下来的短时间内也大概率不会被用到 。
当一个新的页面诞生时,它就像是一个新加入队列的成员,会被添加到 LRU 链表的头部。这是因为新页面刚刚被创建或访问,被认为是最活跃的 。随着时间的推移和进程的不断运行,页面会在链表中逐渐 “老化” 。如果一个页面在一段时间内没有被再次访问,它就会像一个逐渐被遗忘的成员,慢慢向链表的尾部移动 。这是因为它的活跃程度在降低,被认为是不太可能被频繁使用的页面 。
内核就像一个精明的筛选者,会通过 LRU 链表来选择合适的页面进行回收 。当系统内存不足时,链表尾部的页面就成为了被换出的首选候选者 。这是因为它们是最近最少被访问的,回收它们对系统的影响相对较小 。老化机制则像是一个时间计数器,用于判断页面的使用频繁程度 。
页面在 LRU 链表中的位置和停留时间,就是老化机制判断的重要依据 。越靠近链表尾部的页面,停留时间越长,说明它越不活跃,越有可能被回收 。而那些经常被访问的页面,会不断地被移到链表头部,保持着较高的活跃程度,从而避免被回收 。通过 LRU 链表和老化机制的协同工作,Linux 内核能够高效地管理内存页面,确保系统在有限的内存资源下稳定运行 。
2.3第二次机会法
第二次机会法是在LRU算法基础上的一次智慧升级,它就像是给 LRU 算法戴上了一副更精准的眼镜,让页面回收更加合理 。在经典的LRU算法中,虽然它能够根据页面的使用时间来选择换出的页面,但有时会出现一个问题:即使是频繁使用的页面,也可能因为在某一时刻恰好处于LRU链表的尾部而被误回收 。这就好比一个经常被使用的工具,仅仅因为暂时被放在了角落,就差点被当作无用的东西扔掉 。
第二次机会法为了解决这个问题,引入了一个关键的判断依据 —— 访问位 。访问位就像是一个使用记录标签,记录着页面是否被访问过 。当内核需要选择置换页面时,它不再仅仅依赖于页面在 LRU 链表中的位置,而是会先检查页面的访问位 。如果访问位是 0,说明这个页面在一段时间内没有被访问过,就像一个被遗忘的角落,它就有可能被淘汰 。但如果访问位是 1,那就意味着这个页面最近被访问过,它就像是一个刚刚被使用过的工具,会被给予第二次机会,不会被轻易淘汰 。
当一个页面得到第二次机会时,它的访问位会被清 0,然后被移到非活动链表中 。这就像是把这个工具暂时放在一个不太常用的地方,但还保留着它 。如果在此期间,该页又被访问过,访问位将再次被置为 1,就像这个工具又被拿出来使用了 。而且,第二次访问的时候发现这一页的访问位为 1,就会把该页移到活动链表,让它回到更活跃的位置 。这样一来,如果一个页面经常被使用,其访问位总是保持为 1,它就能够一直留在内存中,不会被淘汰出去 。第二次机会法通过这种方式,避免了频繁使用的页面被误回收,大大提高了回收算法的准确性,让 Linux 内核的页面回收机制更加智能和高效 。
2.4反向映射技术
反向映射技术,是 Linux 内核内存管理中的一项关键技术,它就像是一把神奇的钥匙,能够快速打开从物理页面到虚拟地址的大门 。在 Linux 系统中,虚拟内存管理允许每个进程拥有独立的虚拟地址空间,虚拟地址通过页表映射到物理内存 。这就好比一个大型公寓楼,每个房间都有自己的门牌号(虚拟地址),而这些门牌号通过一种映射关系(页表)对应到实际的房间位置(物理内存) 。
 图片
图片
反向映射则是从相反的方向出发,它关注的是已知物理页面时,如何找到映射该物理页面的虚拟地址 。这就像是已知一个实际的房间位置,要找出所有通向这个房间的门牌号 。内核通过维护一个反向映射数据结构来实现这一功能,这个数据结构就像是一个详细的房间使用记录簿,包含了物理页面与其对应的虚拟页面的信息 。
反向映射技术在页面回收中有着至关重要的作用 。当系统需要释放内存时,它就像是一个精准的探测器,允许操作系统判断哪些虚拟地址使用了特定的物理页面,从而决定是否可以安全地回收该页面 。特别是在回收共享页面时,其优势更加明显 。想象一下,多个进程就像是多个租客,他们可能共享同一个房间(共享页面) 。反向映射机制就像是公寓管理员手中的租客名单,能够帮助跟踪这些映射关系,确保在回收页面时,不会影响到其他正在使用该页面的进程 。同时,反向映射技术也极大地提高了页面回收的效率,它避免了遍历整个系统来查找映射关系的繁琐过程,就像直接从租客名单中查找信息一样快速,让 Linux 内核能够更加高效地管理内存资源,保障系统的稳定运行 。基于对象的反向映射的实现:
(1)数据结构
首先,PFRA必须要确定待回收页是共享的还是非共享的,以及是映射页或是匿名页。为做到这一点,内核要查看页描述符的两个字段:_mapcount和mapping。_mapcount字段存放引用页框的页表项数目,确定其是否共享;mapping字段用于确定页是映射的或是匿名的:为空表示该页属于交换高速缓存;非空,且最低位是1,表示该页为匿名页,同时mapping字段中存放的是指向anon_vma描述符的指针;如果mapping字段非空,且最低位是0,表示该页为映射页;同时mapping字段指向对应文件的address_space对象。
复制
struct page
{
atomic_t _mapcount;
union {
……
struct {
……
struct address_space *mapping;
};
……
};1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.
Linux的address_space对象在RAMA中是对其的,所以其起始地址是4的倍数。因此其mapping字段的最低位可以用作一个标志位来表示该字段的指针是指向address_space对象还是anon_vma描述符。PageAnon检查mapping最低位。
复制
/*检查页是否为匿名页,低位为1时为匿名页*/
static inline int PageAnon(struct page *page)
{
return ((unsigned long)page->mapping & PAGE_MAPPING_ANON) != 0;
}1.2.3.4.5.
匿名页面和文件映射页面分别采用了不同的底层数据结构去存放与页面相关的虚拟内存区域。对于匿名页面来说,与该页面相关的虚拟内存区域存放在结构 anon_vma 中定义的双向链表中。结构 anon_vma 定义很简单,如下所示:
复制
struct anon_vma
{
spinlock_t lock;
struct list_head head;
};1.2.3.4.5.
匿名页的面向对象反向映射如下图:
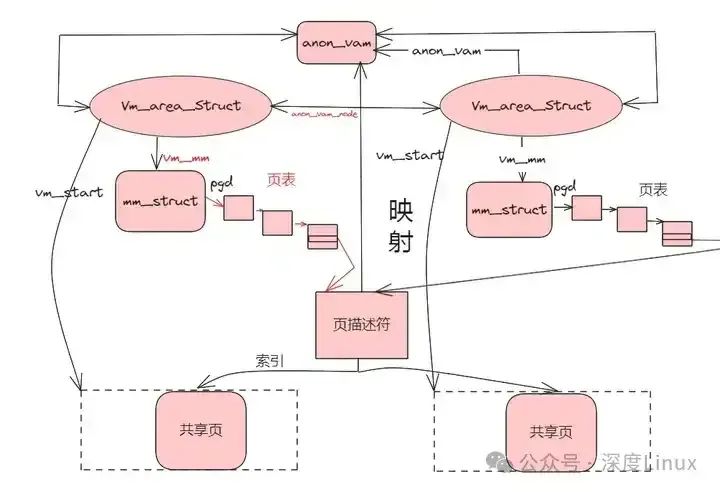 图片
图片
可以通过页面的mapping找到anon_vma然后找到映射该页面的所有线性区域(vm_area_struct结构)。
而对于基于文件映射的页面来说,与匿名页面不同的是,与该页面相关的虚拟内存区域的存放是利用了优先级搜索树这种数据结构的。这是因为对于匿名页面来说,页面虽然可以是共享的,但是一般情况下,共享匿名页面的使用者的数目不会很多;而对于基于文件映射的页面来说,共享页面的使用者的数目可能会非常多,使用优先级搜索树这种结构可以更加快速地定位那些引用了该页面的虚拟内存区域。操作系统会为每一个文件都建立一个优先级搜索树,其根节点可以通过结构 address_space 中的 i_mmap 字段获取。
复制
struct address_space {
……
struct prio_tree_root i_mmap;
……
}1.2.3.4.5.
Linux中使用 (radix,size,heap) 来表示优先级搜索树中的节点。其中,radix 表示内存区域的起始位置,heap 表示内存区域的结束位置,size 与内存区域的大小成正比。在优先级搜索树中,父节点的 heap 值一定不会小于子节点的 heap 值。在树中进行查找时,根据节点的 radix 值进行。程序可以根据 size 值区分那些具有相同 radix 值的节点。
在用于表示虚拟内存区域的结构 vm_area_struct 中,与上边介绍的双向链表和优先级搜索树相关的字段如下所示:
复制
struct vm_area_struct {
struct mm_struct * vm_mm;
……
union {
struct {
struct list_head list;
void *parent;
struct vm_area_struct *head;
} vm_set;
struct raw_prio_tree_node prio_tree_node;
} shared;
struct list_head anon_vma_node;
struct anon_vma *anon_vma;
};1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.
与匿名页面的双向链表相关的字段是 anon_vma_node 和 anon_vma。union shared 则与文件映射页面使用的优先级搜索树相关。字段 anon_vma 指向 anon_vma 表;字段 anon_vma_node 将映射该页面的所有虚拟内存区域链接起来;union shared 中的 prio_tree_node 结构用于表示优先级搜索树的一个节点;
在某些情况下,比如不同的进程的内存区域可能映射到了同一个文件的相同部分,也就是说这些内存区域具有相同的(radix,size,heap)值,这个时候 Linux 就会在树上相应的节点(树上原来那个具有相同(radix,size,heap) 值的内存区域)上接一个双向链表用来存放这些内存区域,这个链表用 vm_set.list 来表示;树上那个节点指向的链表中的第一个节点是表头,用 vm_set.head 表示;vm_set.parent 用于表示是否是树结点。下边给出一个小图示简单说明一下 vm_set.list 和 vm_set.head。
通过结构 vm_area_struct 中的 vm_mm 字段可以找到对应的 mm_struct 结构,在该结构中找到页全局目录,从而定位所有相关的页表项。
(2)反向映射实现
在进行页面回收的时候,Linux的 shrink_page_list() 函数中调用 try_to_unmap() 函数去更新所有引用了回收页面的页表项。其代码流程如下所示:
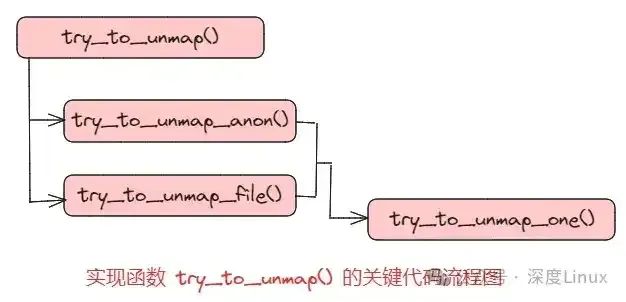 图片
图片
函数 try_to_unmap() 分别调用了两个函数 try_to_unmap_anon() 和 try_to_unmap_file(),其目的都是检查并确定都有哪些页表项引用了同一个物理页面,但是,由于匿名页面和文件映射页面分别采用了不同的数据结构,所以二者采用了不同的方法。
函数 try_to_unmap_anon() 用于匿名页面,该函数扫描相应的 anon_vma 表中包含的所有内存区域,并对这些内存区域分别调用 try_to_unmap_one() 函数。
函数 try_to_unmap_file() 用于文件映射页面,该函数会在优先级搜索树中进行搜索,并为每一个搜索到的内存区域调用 try_to_unmap_one() 函数。
两条代码路径最终汇合到 try_to_unmap_one() 函数中,更新引用特定物理页面的所有页表项的操作都是在这个函数中实现的。
代码如下,对关键部分做了注释:
复制
static int try_to_unmap_anon(struct page *page, enum ttu_flags flags)
{
struct anon_vma *anon_vma;
struct vm_area_struct *vma;
unsigned int mlocked = 0;
int ret = SWAP_AGAIN;
int unlock = TTU_ACTION(flags) == TTU_MUNLOCK;
if (MLOCK_PAGES && unlikely(unlock))
ret = SWAP_SUCCESS; /* default for try_to_munlock() */
/*如果该页面为匿名映射,返回该页面对应的匿名结构*/
anon_vma = page_lock_anon_vma(page);
if (!anon_vma)
return ret;
/*这里可以看出,vma的anon_vma_node字段链接到
anon_vma的head字段*/
/*扫描线性区描述符的anon_vma链表*/
list_for_each_entry(vma, &anon_vma->head, anon_vma_node) {
if (MLOCK_PAGES && unlikely(unlock)) {
if (!((vma->vm_flags & VM_LOCKED) &&
page_mapped_in_vma(page, vma)))
continue; /* must visit all unlocked vmas */
ret = SWAP_MLOCK; /* saw at least one mlocked vma */
} else {
/*对anon_vma链表中的每一个vma线性区描述符
调用该函数*/
ret = try_to_unmap_one(page, vma, flags);
if (ret == SWAP_FAIL || !page_mapped(page))
break;
}
if (ret == SWAP_MLOCK) {
mlocked = try_to_mlock_page(page, vma);
if (mlocked)
break; /* stop if actually mlocked page */
}
}
page_unlock_anon_vma(anon_vma);
if (mlocked)
ret = SWAP_MLOCK; /* actually mlocked the page */
else if (ret == SWAP_MLOCK)
ret = SWAP_AGAIN; /* saw VM_LOCKED vma */
return ret;
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.46.
复制
/*
* Subfunctions of try_to_unmap: try_to_unmap_one called
* repeatedly from either try_to_unmap_anon or try_to_unmap_file.
*/
/**
*page是一个指向目标页描述符的指针;
*vma是指向线性区描述符的指针
*/
static int try_to_unmap_one(struct page *page, struct vm_area_struct *vma,
enum ttu_flags flags)
{
struct mm_struct *mm = vma->vm_mm;
unsigned long address;
pte_t *pte;
pte_t pteval;
spinlock_t *ptl;
int ret = SWAP_AGAIN;
/*计算出待回收页的线性地址*/
address = vma_address(page, vma);
if (address == -EFAULT)
goto out;
/*获取线性地址对应的页表项地址*/
pte = page_check_address(page, mm, address, &ptl, 0);
if (!pte)
goto out;
/*
* If the page is mlock()d, we cannot swap it out.
* If its recently referenced (perhaps page_referenced
* skipped over this mm) then we should reactivate it.
*/
/*下面为判断是否可以被回收*/
if (!(flags & TTU_IGNORE_MLOCK)) {
if (vma->vm_flags & VM_LOCKED) {
ret = SWAP_MLOCK;
goto out_unmap;
}
}
if (!(flags & TTU_IGNORE_ACCESS)) {
if (ptep_clear_flush_young_notify(vma, address, pte)) {
ret = SWAP_FAIL;
goto out_unmap;
}
}
/* Nuke the page table entry. */
flush_cache_page(vma, address, page_to_pfn(page));
/*更新页表项并冲刷相应的TLB*/
pteval = ptep_clear_flush_notify(vma, address, pte);
/* Move the dirty bit to the physical page now the pte is gone. */
if (pte_dirty(pteval))/*如果是脏页面,置位PG_dirty*/
set_page_dirty(page);
/* Update high watermark before we lower rss */
/*更新mm的hiwater_rss*/
update_hiwater_rss(mm);
if (PageHWPoison(page) && !(flags & TTU_IGNORE_HWPOISON)) {
if (PageAnon(page))
dec_mm_counter(mm, anon_rss);
else
dec_mm_counter(mm, file_rss);
set_pte_at(mm, address, pte,
swp_entry_to_pte(make_hwpoison_entry(page)));
} else if (PageAnon(page)) {/*如果是匿名页*/
swp_entry_t entry = { .val = page_private(page) };
if (PageSwapCache(page)) {
/*
* Store the swap location in the pte.
* See handle_pte_fault() ...
*/
/*保存换出位置*/
swap_duplicate(entry);
if (list_empty(&mm->mmlist)) {
spin_lock(&mmlist_lock);
if (list_empty(&mm->mmlist))
/*添加到init_mm的相应链表,从这里可以
看出mm->mmlist为交换用的链表*/
list_add(&mm->mmlist, &init_mm.mmlist);
spin_unlock(&mmlist_lock);
}
dec_mm_counter(mm, anon_rss);
} else if (PAGE_MIGRATION) {
/*
* Store the pfn of the page in a special migration
* pte. do_swap_page() will wait until the migration
* pte is removed and then restart fault handling.
*/
BUG_ON(TTU_ACTION(flags) != TTU_MIGRATION);
entry = make_migration_entry(page, pte_write(pteval));
}
set_pte_at(mm, address, pte, swp_entry_to_pte(entry));
BUG_ON(pte_file(*pte));
} else if (PAGE_MIGRATION && (TTU_ACTION(flags) == TTU_MIGRATION)) {
/* Establish migration entry for a file page */
swp_entry_t entry;
entry = make_migration_entry(page, pte_write(pteval));
set_pte_at(mm, address, pte, swp_entry_to_pte(entry));
} else
dec_mm_counter(mm, file_rss);
/*断开页表项和物理页面的关系*/
page_remove_rmap(page);
/*释放所分配的缓存*/
page_cache_release(page);
out_unmap:
pte_unmap_unlock(pte, ptl);
out:
return ret;
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.46.47.48.49.50.51.52.53.54.55.56.57.58.59.60.61.62.63.64.65.66.67.68.69.70.71.72.73.74.75.76.77.78.79.80.81.82.83.84.85.86.87.88.89.90.91.92.93.94.95.96.97.98.99.100.101.102.103.104.105.106.107.108.109.110.111.112.113.
对于给定的物理页面来说,该函数会根据计算出来的线性地址找到对应的页表项地址,并更新页表项。对于匿名页面来说,换出的位置必须要被保存下来,以便于该页面下次被访问的时候可以被换进来。并非所有的页面都是可以被回收的,比如被 mlock() 函数设置过的内存页,或者最近刚被访问过的页面,等等,都是不可以被回收的。一旦遇上这样的页面,该函数会直接跳出执行并返回错误代码。
如果涉及到页缓存中的数据,需要设置页缓存中的数据无效,必要的时候还要置位页面标识符以进行数据回写。该函数还会更新相应的一些页面使用计数器,比如前边提到的 _mapcount 字段,还会相应地更新进程拥有的物理页面数目等。
三、页面回收机制
当我们申请分配页的时候,页分配器首先尝试使用低水线分配页。如果使用低水线分配失败,说明内存轻微不足,页分配器将会唤醒内存节点的页回收内核线程,异步回收页,然后尝试使用最低水线分配页。如果使用最低水线分配失败,说明内存严重不足,页分配器会直接回收。
针对不同的物理页,采用不同的回收策略:交换支持的页和存储设备支持的文件页。
根据什么原则选择回收物理页
Linux内核使用LRU(Least Recently Used,最近最少使用)算法选择最近最少使用的物理页。回收物理页的时候,如果物理页被映射到进程的虚拟地址空间,那么需要从页表中删除虚拟页到物理页的映射。
3.1LRU数据结构
内存管理子系统使用节点(node),区域(zone)、页(page)三级结构描述物理内存:分别使用内存节点结构体 struct pglist_data,区域结构体struct zone,页结构体struct page表示。在内存节点结构体 struct pglist_data中,有一个struct lruvec结构体,表示lru链表描述符:
复制
typedef struct pglist_data {
......
spinlock_t lru_lock;//lru链表锁
/* Fields commonly accessed by the page reclaim scanner */
struct lruvec lruvec;//lru链表描述符,里面有5个lru链表
......
} pg_data_t;
struct lruvec {
struct list_head lists[NR_LRU_LISTS];//5个lru双向链表头
struct zone_reclaim_stat reclaim_stat; //与回收相关的统计数据
/* Evictions & activations on the inactive file list */
atomic_long_t inactive_age;
/* Refaults at the time of last reclaim cycle */
unsigned long refaults;//记录最后一次回收周期发生的结果
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMCG
struct pglist_data *pgdat;//所属内存节点结构体 struct pglist_data
#endif
};
enum lru_list {
LRU_INACTIVE_ANON = LRU_BASE,
LRU_ACTIVE_ANON = LRU_BASE + LRU_ACTIVE,
LRU_INACTIVE_FILE = LRU_BASE + LRU_FILE,
LRU_ACTIVE_FILE = LRU_BASE + LRU_FILE + LRU_ACTIVE,
LRU_UNEVICTABLE,
NR_LRU_LISTS
};1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.
从上面的enum lru_list中可以看出5个lru链表分别是:
不活动匿名页LRU链表,用来链接不活动的匿名页,即最近访问频率低的匿名页;活动匿名页LRU链表,用来链接活动的匿名页,即最近访问频率高的匿名页;不活动文件页LRU链表,用来链接不活动的文件页,即最近访问频率低的文件页;活动文件页LRU链表,用来链接活动的文件页,即最近访问频率高的文件页;不可回收LRU链表,用来链接使用mlock锁定在内存中、不允许回收的物理页。
复制
//用于页描述符,一组标志(如PG_locked、PG_error),同时页框所在的管理区和node的编号也保存在当中
struct page {
/* 在lru算法中主要用到的标志
* PG_active: 表示此页当前是否活跃,当放到或者准备放到活动lru链表时,被置位
* PG_referenced: 表示此页最近是否被访问,每次页面访问都会被置位
* PG_lru: 表示此页是处于lru链表中的
* PG_mlocked: 表示此页被mlock()锁在内存中,禁止换出和释放
* PG_swapbacked: 表示此页依靠swap,可能是进程的匿名页(堆、栈、数据段),匿名mmap共享内存映射,shmem共享内存映射
*/
unsigned long flags;
......
union {
/* 页处于不同情况时,加入的链表不同
* 1.是一个进程正在使用的页,加入到对应lru链表和lru缓存中
* 2.如果为空闲页框,并且是空闲块的第一个页,加入到伙伴系统的空闲块链表中(只有空闲块的第一个页需要加入)
* 3.如果是一个slab的第一个页,则将其加入到slab链表中(比如slab的满slab链表,slub的部分空slab链表)
* 4.将页隔离时用于加入隔离链表
*/
struct list_head lru;
......
};
......
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.
3.2页回收源码分析
在调用函数进行一次内存分配时:alloc_page → alloc_pages_current → __alloc_pages_nodemask,__alloc_pages_nodemask()这个函数是内存分配的心脏,对内存分配流程做了一个整体的组织。在上面那篇文章中没有详细分析__alloc_pages_slowpath,只是讲解了快速路劲get_page_from_freelist。现在我们详细的看看__alloc_pages_slowpath函数,函数位于mm/page_alloc.c文件中:
复制
static inline struct page *
__alloc_pages_slowpath(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order,
struct alloc_context *ac)
{
bool can_direct_reclaim = gfp_mask & __GFP_DIRECT_RECLAIM;
const bool costly_order = order > PAGE_ALLOC_COSTLY_ORDER;
struct page *page = NULL;
unsigned int alloc_flags;
unsigned long did_some_progress;
enum compact_priority compact_priority;
enum compact_result compact_result;
int compaction_retries;
int no_progress_loops;
unsigned int cpuset_mems_cookie;
int reserve_flags;
/*
* We also sanity check to catch abuse of atomic reserves being used by
* callers that are not in atomic context.
*/
if (WARN_ON_ONCE((gfp_mask & (__GFP_ATOMIC|__GFP_DIRECT_RECLAIM)) ==
(__GFP_ATOMIC|__GFP_DIRECT_RECLAIM)))
gfp_mask &= ~__GFP_ATOMIC;
retry_cpuset:
compaction_retries = 0;
no_progress_loops = 0;
compact_priority = DEF_COMPACT_PRIORITY;
//后面可能会检查cpuset是否允许当前进程从哪些内存节点申请页
cpuset_mems_cookie = read_mems_allowed_begin();
/*
* The fast path uses conservative alloc_flags to succeed only until
* kswapd needs to be woken up, and to avoid the cost of setting up
* alloc_flags precisely. So we do that now.
*/
//把分配标志位转化为内部的分配标志位,调整为最低水线标志
alloc_flags = gfp_to_alloc_flags(gfp_mask);
/*
* We need to recalculate the starting point for the zonelist iterator
* because we might have used different nodemask in the fast path, or
* there was a cpuset modification and we are retrying - otherwise we
* could end up iterating over non-eligible zones endlessly.
*/
//获取首选的内存区域,因为在快速路径中使用了不同的节点掩码,避免再次遍历不合格的区域。
ac->preferred_zoneref = first_zones_zonelist(ac->zonelist,
ac->high_zoneidx, ac->nodemask);
if (!ac->preferred_zoneref->zone)
goto nopage;
//异步回收页,唤醒kswapd内核线程进行页面回收
if (gfp_mask & __GFP_KSWAPD_RECLAIM)
wake_all_kswapds(order, gfp_mask, ac);
/*
* The adjusted alloc_flags might result in immediate success, so try
* that first
*/
//调整alloc_flags后可能会立即申请成功,所以先尝试一下
page = get_page_from_freelist(gfp_mask, order, alloc_flags, ac);
if (page)
goto got_pg;
/*
* For costly allocations, try direct compaction first, as its likely
* that we have enough base pages and dont need to reclaim. For non-
* movable high-order allocations, do that as well, as compaction will
* try prevent permanent fragmentation by migrating from blocks of the
* same migratetype.
* Dont try this for allocations that are allowed to ignore
* watermarks, as the ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS attempt didnt yet happen.
*/
//申请阶数大于0,不可移动的位于高阶的,忽略水位线的
if (can_direct_reclaim &&
(costly_order ||
(order > 0 && ac->migratetype != MIGRATE_MOVABLE))
&& !gfp_pfmemalloc_allowed(gfp_mask)) {
//尝试内存压缩,进行页面迁移,然后进行页面分配
page = __alloc_pages_direct_compact(gfp_mask, order,
alloc_flags, ac,
INIT_COMPACT_PRIORITY,
&compact_result);
if (page)
goto got_pg;
/*
* Checks for costly allocations with __GFP_NORETRY, which
* includes THP page fault allocations
*/
if (costly_order && (gfp_mask & __GFP_NORETRY)) {
/*
* If compaction is deferred for high-order allocations,
* it is because sync compaction recently failed. If
* this is the case and the caller requested a THP
* allocation, we do not want to heavily disrupt the
* system, so we fail the allocation instead of entering
* direct reclaim.
*/
if (compact_result == COMPACT_DEFERRED)
goto nopage;
/*
* Looks like reclaim/compaction is worth trying, but
* sync compaction could be very expensive, so keep
* using async compaction.
*/
//同步压缩非常昂贵,所以继续使用异步压缩
compact_priority = INIT_COMPACT_PRIORITY;
}
}
retry:
/* Ensure kswapd doesnt accidentally go to sleep as long as we loop */
//如果页回收线程意外睡眠则再次唤醒,确保交换线程没有意外
if (gfp_mask & __GFP_KSWAPD_RECLAIM)
wake_all_kswapds(order, gfp_mask, ac);
//如果调用者承若给我们紧急内存使用,我们就忽略水线,进行无水线分配
reserve_flags = __gfp_pfmemalloc_flags(gfp_mask);
if (reserve_flags)
alloc_flags = reserve_flags;
/*
* Reset the nodemask and zonelist iterators if memory policies can be
* ignored. These allocations are high priority and system rather than
* user oriented.
*/
//如果可以忽略内存策略,则重置nodemask和zonelist
if (!(alloc_flags & ALLOC_CPUSET) || reserve_flags) {
ac->nodemask = NULL;
ac->preferred_zoneref = first_zones_zonelist(ac->zonelist,
ac->high_zoneidx, ac->nodemask);
}
/* Attempt with potentially adjusted zonelist and alloc_flags */
//尝试使用可能调整的区域备用列表和分配标志
page = get_page_from_freelist(gfp_mask, order, alloc_flags, ac);
if (page)
goto got_pg;
/* Caller is not willing to reclaim, we cant balance anything */
//如果不可以直接回收,则申请失败
if (!can_direct_reclaim)
goto nopage;
/* Avoid recursion of direct reclaim */
if (current->flags & PF_MEMALLOC)
goto nopage;
/* Try direct reclaim and then allocating */
//直接页面回收,然后进行页面分配
page = __alloc_pages_direct_reclaim(gfp_mask, order, alloc_flags, ac,
&did_some_progress);
if (page)
goto got_pg;
/* Try direct compaction and then allocating */
//进行页面压缩,然后进行页面分配
page = __alloc_pages_direct_compact(gfp_mask, order, alloc_flags, ac,
compact_priority, &compact_result);
if (page)
goto got_pg;
/* Do not loop if specifically requested */
//如果调用者要求不要重试,则放弃
if (gfp_mask & __GFP_NORETRY)
goto nopage;
/*
* Do not retry costly high order allocations unless they are
* __GFP_RETRY_MAYFAIL
*/
//不要重试代价高昂的高阶分配,除非它们是__GFP_RETRY_MAYFAIL
if (costly_order && !(gfp_mask & __GFP_RETRY_MAYFAIL))
goto nopage;
//重新尝试回收页
if (should_reclaim_retry(gfp_mask, order, ac, alloc_flags,
did_some_progress > 0, &no_progress_loops))
goto retry;
/*
* It doesnt make any sense to retry for the compaction if the order-0
* reclaim is not able to make any progress because the current
* implementation of the compaction depends on the sufficient amount
* of free memory (see __compaction_suitable)
*/
//如果申请阶数大于0,判断是否需要重新尝试压缩
if (did_some_progress > 0 &&
should_compact_retry(ac, order, alloc_flags,
compact_result, &compact_priority,
&compaction_retries))
goto retry;
/* Deal with possible cpuset update races before we start OOM killing */
//如果cpuset允许修改内存节点申请就修改
if (check_retry_cpuset(cpuset_mems_cookie, ac))
goto retry_cpuset;
/* Reclaim has failed us, start killing things */
//使用oom选择一个进程杀死
page = __alloc_pages_may_oom(gfp_mask, order, ac, &did_some_progress);
if (page)
goto got_pg;
/* Avoid allocations with no watermarks from looping endlessly */
//如果当前进程是oom选择的进程,并且忽略了水线,则放弃申请
if (tsk_is_oom_victim(current) &&
(alloc_flags == ALLOC_OOM ||
(gfp_mask & __GFP_NOMEMALLOC)))
goto nopage;
/* Retry as long as the OOM killer is making progress */
//如果OOM杀手正在取得进展,再试一次
if (did_some_progress) {
no_progress_loops = 0;
goto retry;
}
nopage:
/* Deal with possible cpuset update races before we fail */
if (check_retry_cpuset(cpuset_mems_cookie, ac))
goto retry_cpuset;
/*
* Make sure that __GFP_NOFAIL request doesnt leak out and make sure
* we always retry
*/
if (gfp_mask & __GFP_NOFAIL) {
/*
* All existing users of the __GFP_NOFAIL are blockable, so warn
* of any new users that actually require GFP_NOWAIT
*/
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(!can_direct_reclaim))
goto fail;
/*
* PF_MEMALLOC request from this context is rather bizarre
* because we cannot reclaim anything and only can loop waiting
* for somebody to do a work for us
*/
WARN_ON_ONCE(current->flags & PF_MEMALLOC);
/*
* non failing costly orders are a hard requirement which we
* are not prepared for much so lets warn about these users
* so that we can identify them and convert them to something
* else.
*/
WARN_ON_ONCE(order > PAGE_ALLOC_COSTLY_ORDER);
/*
* Help non-failing allocations by giving them access to memory
* reserves but do not use ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS because this
* could deplete whole memory reserves which would just make
* the situation worse
*/
//允许它们访问内存备用列表
page = __alloc_pages_cpuset_fallback(gfp_mask, order, ALLOC_HARDER, ac);
if (page)
goto got_pg;
cond_resched();
goto retry;
}
fail:
warn_alloc(gfp_mask, ac->nodemask,
"page allocation failure: order:%u", order);
got_pg:
return page;
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.46.47.48.49.50.51.52.53.54.55.56.57.58.59.60.61.62.63.64.65.66.67.68.69.70.71.72.73.74.75.76.77.78.79.80.81.82.83.84.85.86.87.88.89.90.91.92.93.94.95.96.97.98.99.100.101.102.103.104.105.106.107.108.109.110.111.112.113.114.115.116.117.118.119.120.121.122.123.124.125.126.127.128.129.130.131.132.133.134.135.136.137.138.139.140.141.142.143.144.145.146.147.148.149.150.151.152.153.154.155.156.157.158.159.160.161.162.163.164.165.166.167.168.169.170.171.172.173.174.175.176.177.178.179.180.181.182.183.184.185.186.187.188.189.190.191.192.193.194.195.196.197.198.199.200.201.202.203.204.205.206.207.208.209.210.211.212.213.214.215.216.217.218.219.220.221.222.223.224.225.226.227.228.229.230.231.232.233.234.235.236.237.238.239.240.241.242.243.244.245.246.247.248.249.250.251.252.253.254.255.256.257.258.259.260.261.262.263.264.265.266.267.268.269.270.271.272.273.
上面代码可以看出,在慢速路径上系统做了很多判断,wake_all_kswapdsb是唤醒一个异步回收内存的线程,他有着自己的初始化函数。
3.3直接页面回收
在慢速回收路径中,首先是启动异步回收,异步回收失败后,就是下面准备讲解的内存直接回收了。直接页面回收过程分析,函数入口为__alloc_pages_direct_reclaim,函数位于mm/page_alloc.c文件中:
复制
static inline struct page *
__alloc_pages_direct_reclaim(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order,
unsigned int alloc_flags, const struct alloc_context *ac,
unsigned long *did_some_progress)
{
struct page *page = NULL;
bool drained = false;
//真正缓慢的分配路径,直接同步页面回收
*did_some_progress = __perform_reclaim(gfp_mask, order, ac);
if (unlikely(!(*did_some_progress)))
return NULL;
retry:
//进行页面分配操作
page = get_page_from_freelist(gfp_mask, order, alloc_flags, ac);
/*
* If an allocation failed after direct reclaim, it could be because
* pages are pinned on the per-cpu lists or in high alloc reserves.
* Shrink them them and try again
*/
//如果在直接回收之后分配失败,可能是因为页面固定在每个cpu列表上或处于高分配预留中
if (!page && !drained) {
unreserve_highatomic_pageblock(ac, false);//unreserve处于高分配预留中的内存
drain_all_pages(NULL);//释放固定在每个cpu列表上页面
drained = true;
goto retry;//再试一次慢路径回收,分配内存
}
return page;
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.
__alloc_pages_direct_reclaim会调用__perform_reclaim进行直接同步页面回收,再通过get_page_from_freelist分配页面,__perform_reclaim:
复制
static int
__perform_reclaim(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order,
const struct alloc_context *ac)
{
struct reclaim_state reclaim_state;
int progress;
unsigned int noreclaim_flag;
cond_resched();//主动让出cpu
/* We now go into synchronous reclaim */
cpuset_memory_pressure_bump();//计算内存压力
fs_reclaim_acquire(gfp_mask);
noreclaim_flag = memalloc_noreclaim_save();//保存内存标志
reclaim_state.reclaimed_slab = 0;
current->reclaim_state = &reclaim_state;
//直接页面回收
progress = try_to_free_pages(ac->zonelist, order, gfp_mask,
ac->nodemask);
current->reclaim_state = NULL;
memalloc_noreclaim_restore(noreclaim_flag);//恢复内存标志
fs_reclaim_release(gfp_mask);
cond_resched();
return progress;
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.
__perform_reclaim保存一下环境后通过try_to_free_pages来进行直接页面回收。
try_to_free_pages函数位于mm/vmscan.c文件:
复制
unsigned long try_to_free_pages(struct zonelist *zonelist, int order,
gfp_t gfp_mask, nodemask_t *nodemask)
{
unsigned long nr_reclaimed;
struct scan_control sc = {
.nr_to_reclaim = SWAP_CLUSTER_MAX,
.gfp_mask = current_gfp_context(gfp_mask),
.reclaim_idx = gfp_zone(gfp_mask),
.order = order,
.nodemask = nodemask,
.priority = DEF_PRIORITY,
.may_writepage = !laptop_mode,
.may_unmap = 1,
.may_swap = 1,
};
/*
* scan_control uses s8 fields for order, priority, and reclaim_idx.
* Confirm they are large enough for max values.
*/
BUILD_BUG_ON(MAX_ORDER > S8_MAX);
BUILD_BUG_ON(DEF_PRIORITY > S8_MAX);
BUILD_BUG_ON(MAX_NR_ZONES > S8_MAX);
/*
* Do not enter reclaim if fatal signal was delivered while throttled.
* 1 is returned so that the page allocator does not OOM kill at this
* point.
*/
//如果在节流时发送了致命信号,不要进入回收,返回1
if (throttle_direct_reclaim(sc.gfp_mask, zonelist, nodemask))
return 1;
trace_mm_vmscan_direct_reclaim_begin(order,
sc.may_writepage,
sc.gfp_mask,
sc.reclaim_idx);
//这是直接页面回收的主要入口点
nr_reclaimed = do_try_to_free_pages(zonelist, &sc);
trace_mm_vmscan_direct_reclaim_end(nr_reclaimed);
return nr_reclaimed;
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.
try_to_free_pages的真正调用do_try_to_free_pages:
复制
static unsigned long do_try_to_free_pages(struct zonelist *zonelist,
struct scan_control *sc)
{
int initial_priority = sc->priority;
pg_data_t *last_pgdat;
struct zoneref *z;
struct zone *zone;
retry:
delayacct_freepages_start();
if (global_reclaim(sc))//如果当前进行的是全局页回收
__count_zid_vm_events(ALLOCSTALL, sc->reclaim_idx, 1);
do {
//通过reclaimer priority level来计算虚拟内存压力
vmpressure_prio(sc->gfp_mask, sc->target_mem_cgroup,
sc->priority);
sc->nr_scanned = 0;
shrink_zones(zonelist, sc);//页面分配进程的直接回收路径
if (sc->nr_reclaimed >= sc->nr_to_reclaim)
break;
if (sc->compaction_ready)
break;
/*
* If were getting trouble reclaiming, start doing
* writepage even in laptop mode.
*/
//回收过程中遇到了麻烦,则需要回写。
if (sc->priority < DEF_PRIORITY - 2)
sc->may_writepage = 1;
} while (--sc->priority >= 0);
last_pgdat = NULL;
//扫描每一个区域,如果充满了固定的页面,则放弃它
for_each_zone_zonelist_nodemask(zone, z, zonelist, sc->reclaim_idx,
sc->nodemask) {
if (zone->zone_pgdat == last_pgdat)
continue;
last_pgdat = zone->zone_pgdat;
snapshot_refaults(sc->target_mem_cgroup, zone->zone_pgdat);
set_memcg_congestion(last_pgdat, sc->target_mem_cgroup, false);
}
delayacct_freepages_end();
if (sc->nr_reclaimed)//直接回收页数为0则返回
return sc->nr_reclaimed;
/* Aborted reclaim to try compaction? dont OOM, then */
//如果可以压缩规整,则取消回收以尝试压缩
if (sc->compaction_ready)
return 1;
/* Untapped cgroup reserves? Dont OOM, retry. */
if (sc->memcg_low_skipped) {
sc->priority = initial_priority;
sc->memcg_low_reclaim = 1;
sc->memcg_low_skipped = 0;
goto retry;
}
return 0;
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.46.47.48.49.50.51.52.53.54.55.56.57.58.59.60.61.62.63.64.65.66.
do_try_to_free_pages调用shrink_zones这个直接回收路径:
复制
static void shrink_zones(struct zonelist *zonelist, struct scan_control *sc)
{
struct zoneref *z;
struct zone *zone;
unsigned long nr_soft_reclaimed;
unsigned long nr_soft_scanned;
gfp_t orig_mask;
pg_data_t *last_pgdat = NULL;
/*
* If the number of buffer_heads in the machine exceeds the maximum
* allowed level, force direct reclaim to scan the highmem zone as
* highmem pages could be pinning lowmem pages storing buffer_heads
*/
orig_mask = sc->gfp_mask;
if (buffer_heads_over_limit) {
sc->gfp_mask |= __GFP_HIGHMEM;
sc->reclaim_idx = gfp_zone(sc->gfp_mask);
}
for_each_zone_zonelist_nodemask(zone, z, zonelist,
sc->reclaim_idx, sc->nodemask) {
/*
* Take care memory controller reclaiming has small influence
* to global LRU.
*/
if (global_reclaim(sc)) {//如果当前进行的是全局页回收
if (!cpuset_zone_allowed(zone,
GFP_KERNEL | __GFP_HARDWALL))
continue;
/*
* If we already have plenty of memory free for
* compaction in this zone, dont free any more.
* Even though compaction is invoked for any
* non-zero order, only frequent costly order
* reclamation is disruptive enough to become a
* noticeable problem, like transparent huge
* page allocations.
*/
//如果可以压缩规整,并且有足够空间
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_COMPACTION) &&
sc->order > PAGE_ALLOC_COSTLY_ORDER &&
compaction_ready(zone, sc)) {
sc->compaction_ready = true;
continue;
}
/*
* Shrink each node in the zonelist once. If the
* zonelist is ordered by zone (not the default) then a
* node may be shrunk multiple times but in that case
* the user prefers lower zones being preserved.
*/
if (zone->zone_pgdat == last_pgdat)
continue;
/*
* This steals pages from memory cgroups over softlimit
* and returns the number of reclaimed pages and
* scanned pages. This works for global memory pressure
* and balancing, not for a memcgs limit.
*/
nr_soft_scanned = 0;
nr_soft_reclaimed = mem_cgroup_soft_limit_reclaim(zone->zone_pgdat,
sc->order, sc->gfp_mask,
&nr_soft_scanned);
sc->nr_reclaimed += nr_soft_reclaimed;
sc->nr_scanned += nr_soft_scanned;
/* need some check for avoid more shrink_zone() */
}
/* See comment about same check for global reclaim above */
if (zone->zone_pgdat == last_pgdat)
continue;
last_pgdat = zone->zone_pgdat;
shrink_node(zone->zone_pgdat, sc);
}
/*
* Restore to original mask to avoid the impact on the caller if we
* promoted it to __GFP_HIGHMEM.
*/
sc->gfp_mask = orig_mask;//恢复到原来的掩码
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.46.47.48.49.50.51.52.53.54.55.56.57.58.59.60.61.62.63.64.65.66.67.68.69.70.71.72.73.74.75.76.77.78.79.80.81.82.83.84.85.
shrink_zones主要通过shrink_node:
复制
static bool shrink_node(pg_data_t *pgdat, struct scan_control *sc)
{
struct reclaim_state *reclaim_state = current->reclaim_state;
unsigned long nr_reclaimed, nr_scanned;
bool reclaimable = false;
do {
struct mem_cgroup *root = sc->target_mem_cgroup;
struct mem_cgroup_reclaim_cookie reclaim = {
.pgdat = pgdat,
.priority = sc->priority,
};
unsigned long node_lru_pages = 0;
struct mem_cgroup *memcg;
memset(&sc->nr, 0, sizeof(sc->nr));
nr_reclaimed = sc->nr_reclaimed;
nr_scanned = sc->nr_scanned;
memcg = mem_cgroup_iter(root, NULL, &reclaim);
do {
unsigned long lru_pages;
unsigned long reclaimed;
unsigned long scanned;
switch (mem_cgroup_protected(root, memcg)) {
case MEMCG_PROT_MIN:
/*
* Hard protection.
* If there is no reclaimable memory, OOM.
*/
continue;
case MEMCG_PROT_LOW:
/*
* Soft protection.
* Respect the protection only as long as
* there is an unprotected supply
* of reclaimable memory from other cgroups.
*/
if (!sc->memcg_low_reclaim) {
sc->memcg_low_skipped = 1;
continue;
}
memcg_memory_event(memcg, MEMCG_LOW);
break;
case MEMCG_PROT_NONE:
break;
}
reclaimed = sc->nr_reclaimed;
scanned = sc->nr_scanned;
//每个节点页回收的基本操作函数
shrink_node_memcg(pgdat, memcg, sc, &lru_pages);
node_lru_pages += lru_pages;
shrink_slab(sc->gfp_mask, pgdat->node_id,
memcg, sc->priority);
/* Record the groups reclaim efficiency */
//测量虚拟内存的压力,用于记录回收效率
vmpressure(sc->gfp_mask, memcg, false,
sc->nr_scanned - scanned,
sc->nr_reclaimed - reclaimed);
/*
* Direct reclaim and kswapd have to scan all memory
* cgroups to fulfill the overall scan target for the
* node.
*
* Limit reclaim, on the other hand, only cares about
* nr_to_reclaim pages to be reclaimed and it will
* retry with decreasing priority if one round over the
* whole hierarchy is not sufficient.
*/
if (!global_reclaim(sc) &&
sc->nr_reclaimed >= sc->nr_to_reclaim) {
mem_cgroup_iter_break(root, memcg);
break;
}
} while ((memcg = mem_cgroup_iter(root, memcg, &reclaim)));
if (reclaim_state) {
sc->nr_reclaimed += reclaim_state->reclaimed_slab;
reclaim_state->reclaimed_slab = 0;
}
/* Record the subtrees reclaim efficiency */
//测量虚拟内存的压力,用于记录回收效率
vmpressure(sc->gfp_mask, sc->target_mem_cgroup, true,
sc->nr_scanned - nr_scanned,
sc->nr_reclaimed - nr_reclaimed);
if (sc->nr_reclaimed - nr_reclaimed)
reclaimable = true;
if (current_is_kswapd()) {
/*
* If reclaim is isolating dirty pages under writeback,
* it implies that the long-lived page allocation rate
* is exceeding the page laundering rate. Either the
* global limits are not being effective at throttling
* processes due to the page distribution throughout
* zones or there is heavy usage of a slow backing
* device. The only option is to throttle from reclaim
* context which is not ideal as there is no guarantee
* the dirtying process is throttled in the same way
* balance_dirty_pages() manages.
*
* Once a node is flagged PGDAT_WRITEBACK, kswapd will
* count the number of pages under pages flagged for
* immediate reclaim and stall if any are encountered
* in the nr_immediate check below.
*/
if (sc->nr.writeback && sc->nr.writeback == sc->nr.taken)
set_bit(PGDAT_WRITEBACK, &pgdat->flags);
/*
* Tag a node as congested if all the dirty pages
* scanned were backed by a congested BDI and
* wait_iff_congested will stall.
*/
if (sc->nr.dirty && sc->nr.dirty == sc->nr.congested)
set_bit(PGDAT_CONGESTED, &pgdat->flags);
/* Allow kswapd to start writing pages during reclaim.*/
if (sc->nr.unqueued_dirty == sc->nr.file_taken)
set_bit(PGDAT_DIRTY, &pgdat->flags);
/*
* If kswapd scans pages marked marked for immediate
* reclaim and under writeback (nr_immediate), it
* implies that pages are cycling through the LRU
* faster than they are written so also forcibly stall.
*/
if (sc->nr.immediate)
congestion_wait(BLK_RW_ASYNC, HZ/10);
}
/*
* Legacy memcg will stall in page writeback so avoid forcibly
* stalling in wait_iff_congested().
*/
if (!global_reclaim(sc) && sane_reclaim(sc) &&
sc->nr.dirty && sc->nr.dirty == sc->nr.congested)
set_memcg_congestion(pgdat, root, true);
/*
* Stall direct reclaim for IO completions if underlying BDIs
* and node is congested. Allow kswapd to continue until it
* starts encountering unqueued dirty pages or cycling through
* the LRU too quickly.
*/
if (!sc->hibernation_mode && !current_is_kswapd() &&
current_may_throttle() && pgdat_memcg_congested(pgdat, root))
wait_iff_congested(BLK_RW_ASYNC, HZ/10);
} while (should_continue_reclaim(pgdat, sc->nr_reclaimed - nr_reclaimed,
sc->nr_scanned - nr_scanned, sc));
/*
* Kswapd gives up on balancing particular nodes after too
* many failures to reclaim anything from them and goes to
* sleep. On reclaim progress, reset the failure counter. A
* successful direct reclaim run will revive a dormant kswapd.
*/
if (reclaimable)
pgdat->kswapd_failures = 0;
return reclaimable;
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.46.47.48.49.50.51.52.53.54.55.56.57.58.59.60.61.62.63.64.65.66.67.68.69.70.71.72.73.74.75.76.77.78.79.80.81.82.83.84.85.86.87.88.89.90.91.92.93.94.95.96.97.98.99.100.101.102.103.104.105.106.107.108.109.110.111.112.113.114.115.116.117.118.119.120.121.122.123.124.125.126.127.128.129.130.131.132.133.134.135.136.137.138.139.140.141.142.143.144.145.146.147.148.149.150.151.152.153.154.155.156.157.158.159.160.161.162.163.164.165.166.167.168.169.170.171.172.
shrink_node调用shrink_node_memcg:
复制
static void shrink_node_memcg(struct pglist_data *pgdat, struct mem_cgroup *memcg,
struct scan_control *sc, unsigned long *lru_pages)
{
struct lruvec *lruvec = mem_cgroup_lruvec(pgdat, memcg);
unsigned long nr[NR_LRU_LISTS];
unsigned long targets[NR_LRU_LISTS];
unsigned long nr_to_scan;
enum lru_list lru;
unsigned long nr_reclaimed = 0;
unsigned long nr_to_reclaim = sc->nr_to_reclaim;
struct blk_plug plug;
bool scan_adjusted;
//记录原始扫描目标,以便以后进行比例调整
get_scan_count(lruvec, memcg, sc, nr, lru_pages);
/* Record the original scan target for proportional adjustments later */
memcpy(targets, nr, sizeof(nr));
/*
* Global reclaiming within direct reclaim at DEF_PRIORITY is a normal
* event that can occur when there is little memory pressure e.g.
* multiple streaming readers/writers. Hence, we do not abort scanning
* when the requested number of pages are reclaimed when scanning at
* DEF_PRIORITY on the assumption that the fact we are direct
* reclaiming implies that kswapd is not keeping up and it is best to
* do a batch of work at once. For memcg reclaim one check is made to
* abort proportional reclaim if either the file or anon lru has already
* dropped to zero at the first pass.
*/
scan_adjusted = (global_reclaim(sc) && !current_is_kswapd() &&
sc->priority == DEF_PRIORITY);
blk_start_plug(&plug);// 初始化blk_plug并在task_struct内跟踪它,一旦阻塞则刷新挂起任务
while (nr[LRU_INACTIVE_ANON] || nr[LRU_ACTIVE_FILE] ||
nr[LRU_INACTIVE_FILE]) {
unsigned long nr_anon, nr_file, percentage;
unsigned long nr_scanned;
for_each_evictable_lru(lru) {
if (nr[lru]) {
nr_to_scan = min(nr[lru], SWAP_CLUSTER_MAX);
nr[lru] -= nr_to_scan;
nr_reclaimed += shrink_list(lru, nr_to_scan,
lruvec, memcg, sc);
}
}
cond_resched();
if (nr_reclaimed < nr_to_reclaim || scan_adjusted)
continue;
/*
* For kswapd and memcg, reclaim at least the number of pages
* requested. Ensure that the anon and file LRUs are scanned
* proportionally what was requested by get_scan_count(). We
* stop reclaiming one LRU and reduce the amount scanning
* proportional to the original scan target.
*/
nr_file = nr[LRU_INACTIVE_FILE] + nr[LRU_ACTIVE_FILE];
nr_anon = nr[LRU_INACTIVE_ANON] + nr[LRU_ACTIVE_ANON];
/*
* Its just vindictive to attack the larger once the smaller
* has gone to zero. And given the way we stop scanning the
* smaller below, this makes sure that we only make one nudge
* towards proportionality once weve got nr_to_reclaim.
*/
if (!nr_file || !nr_anon)
break;
if (nr_file > nr_anon) {
unsigned long scan_target = targets[LRU_INACTIVE_ANON] +
targets[LRU_ACTIVE_ANON] + 1;
lru = LRU_BASE;
percentage = nr_anon * 100 / scan_target;
} else {
unsigned long scan_target = targets[LRU_INACTIVE_FILE] +
targets[LRU_ACTIVE_FILE] + 1;
lru = LRU_FILE;
percentage = nr_file * 100 / scan_target;
}
/* Stop scanning the smaller of the LRU */
nr[lru] = 0;
nr[lru + LRU_ACTIVE] = 0;
/*
* Recalculate the other LRU scan count based on its original
* scan target and the percentage scanning already complete
*/
lru = (lru == LRU_FILE) ? LRU_BASE : LRU_FILE;
nr_scanned = targets[lru] - nr[lru];
nr[lru] = targets[lru] * (100 - percentage) / 100;
nr[lru] -= min(nr[lru], nr_scanned);
lru += LRU_ACTIVE;
nr_scanned = targets[lru] - nr[lru];
nr[lru] = targets[lru] * (100 - percentage) / 100;
nr[lru] -= min(nr[lru], nr_scanned);
scan_adjusted = true;
}
blk_finish_plug(&plug);
sc->nr_reclaimed += nr_reclaimed;
/*
* Even if we did not try to evict anon pages at all, we want to
* rebalance the anon lru active/inactive ratio.
*/
//如果lru活动页和不活动页比例不平衡
if (inactive_list_is_low(lruvec, false, memcg, sc, true))
//调整lru活动页和不活动页比例
shrink_active_list(SWAP_CLUSTER_MAX, lruvec,
sc, LRU_ACTIVE_ANON);
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.46.47.48.49.50.51.52.53.54.55.56.57.58.59.60.61.62.63.64.65.66.67.68.69.70.71.72.73.74.75.76.77.78.79.80.81.82.83.84.85.86.87.88.89.90.91.92.93.94.95.96.97.98.99.100.101.102.103.104.105.106.107.108.109.110.111.112.113.114.115.116.117.118.
shrink_node_memcg主要调用shrink_list:
复制
static unsigned long shrink_list(enum lru_list lru, unsigned long nr_to_scan,
struct lruvec *lruvec, struct mem_cgroup *memcg,
struct scan_control *sc)
{
if (is_active_lru(lru)) {
//如果lru活动页和不活动页比例不平衡
if (inactive_list_is_low(lruvec, is_file_lru(lru),
memcg, sc, true))
shrink_active_list(nr_to_scan, lruvec, sc, lru);//调整lru活动页和不活动页比例
return 0;
}
return shrink_inactive_list(nr_to_scan, lruvec, sc, lru);//收缩lru不活动页列表,返回直接回收的页数量
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.
shrink_list主要调用shrink_inactive_list:
复制
static noinline_for_stack unsigned long
shrink_inactive_list(unsigned long nr_to_scan, struct lruvec *lruvec,
struct scan_control *sc, enum lru_list lru)
{
LIST_HEAD(page_list);
unsigned long nr_scanned;
unsigned long nr_reclaimed = 0;
unsigned long nr_taken;
struct reclaim_stat stat = {};
isolate_mode_t isolate_mode = 0;
int file = is_file_lru(lru);
struct pglist_data *pgdat = lruvec_pgdat(lruvec);
struct zone_reclaim_stat *reclaim_stat = &lruvec->reclaim_stat;
bool stalled = false;
//如果隔离页太多
while (unlikely(too_many_isolated(pgdat, file, sc))) {
if (stalled)
return 0;
/* wait a bit for the reclaimer. */
msleep(100);//休眠等待一下回收器
stalled = true;
/* We are about to die and free our memory. Return now. */
if (fatal_signal_pending(current))
return SWAP_CLUSTER_MAX;
}
lru_add_drain();
if (!sc->may_unmap)
isolate_mode |= ISOLATE_UNMAPPED;
spin_lock_irq(&pgdat->lru_lock);
//从不活动页链表的尾部取指定页数添加到临时链表page_list中
nr_taken = isolate_lru_pages(nr_to_scan, lruvec, &page_list,
&nr_scanned, sc, isolate_mode, lru);
//做相关统计信息和更新操作
__mod_node_page_state(pgdat, NR_ISOLATED_ANON + file, nr_taken);
reclaim_stat->recent_scanned[file] += nr_taken;
if (current_is_kswapd()) {
if (global_reclaim(sc))
__count_vm_events(PGSCAN_KSWAPD, nr_scanned);
count_memcg_events(lruvec_memcg(lruvec), PGSCAN_KSWAPD,
nr_scanned);
} else {
if (global_reclaim(sc))
__count_vm_events(PGSCAN_DIRECT, nr_scanned);
count_memcg_events(lruvec_memcg(lruvec), PGSCAN_DIRECT,
nr_scanned);
}
spin_unlock_irq(&pgdat->lru_lock);
if (nr_taken == 0)
return 0;
//处理临时链表page_list的所有页
nr_reclaimed = shrink_page_list(&page_list, pgdat, sc, 0,
&stat, false);
spin_lock_irq(&pgdat->lru_lock);
if (current_is_kswapd()) {
if (global_reclaim(sc))
__count_vm_events(PGSTEAL_KSWAPD, nr_reclaimed);
count_memcg_events(lruvec_memcg(lruvec), PGSTEAL_KSWAPD,
nr_reclaimed);
} else {
if (global_reclaim(sc))
__count_vm_events(PGSTEAL_DIRECT, nr_reclaimed);
count_memcg_events(lruvec_memcg(lruvec), PGSTEAL_DIRECT,
nr_reclaimed);
}
//将部分不活动页转化为活动页并且放入活动页链表中
putback_inactive_pages(lruvec, &page_list);
__mod_node_page_state(pgdat, NR_ISOLATED_ANON + file, -nr_taken);
spin_unlock_irq(&pgdat->lru_lock);
mem_cgroup_uncharge_list(&page_list);
//释放引用为0的顺序页面列表
free_unref_page_list(&page_list);
/*
* If dirty pages are scanned that are not queued for IO, it
* implies that flushers are not doing their job. This can
* happen when memory pressure pushes dirty pages to the end of
* the LRU before the dirty limits are breached and the dirty
* data has expired. It can also happen when the proportion of
* dirty pages grows not through writes but through memory
* pressure reclaiming all the clean cache. And in some cases,
* the flushers simply cannot keep up with the allocation
* rate. Nudge the flusher threads in case they are asleep.
*/
//如果脏页队列没有IO等待,则唤醒flusher冲刷线程将数据回写磁盘
if (stat.nr_unqueued_dirty == nr_taken)
wakeup_flusher_threads(WB_REASON_VMSCAN);
sc->nr.dirty += stat.nr_dirty;
sc->nr.congested += stat.nr_congested;
sc->nr.unqueued_dirty += stat.nr_unqueued_dirty;
sc->nr.writeback += stat.nr_writeback;
sc->nr.immediate += stat.nr_immediate;
sc->nr.taken += nr_taken;
if (file)
sc->nr.file_taken += nr_taken;
trace_mm_vmscan_lru_shrink_inactive(pgdat->node_id,
nr_scanned, nr_reclaimed, &stat, sc->priority, file);
return nr_reclaimed;
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.46.47.48.49.50.51.52.53.54.55.56.57.58.59.60.61.62.63.64.65.66.67.68.69.70.71.72.73.74.75.76.77.78.79.80.81.82.83.84.85.86.87.88.89.90.91.92.93.94.95.96.97.98.99.100.101.102.103.104.105.106.107.108.109.110.111.112.113.114.115.116.117.118.
shrink_inactive_list主要调用shrink_page_list:
复制
static unsigned long shrink_page_list(struct list_head *page_list,
struct pglist_data *pgdat,
struct scan_control *sc,
enum ttu_flags ttu_flags,
struct reclaim_stat *stat,
bool force_reclaim)
{
LIST_HEAD(ret_pages);
LIST_HEAD(free_pages);
int pgactivate = 0;
unsigned nr_unqueued_dirty = 0;
unsigned nr_dirty = 0;
unsigned nr_congested = 0;
unsigned nr_reclaimed = 0;
unsigned nr_writeback = 0;
unsigned nr_immediate = 0;
unsigned nr_ref_keep = 0;
unsigned nr_unmap_fail = 0;
cond_resched();
//遍历临时链表page_list
while (!list_empty(page_list)) {
struct address_space *mapping;
struct page *page;
int may_enter_fs;
enum page_references references = PAGEREF_RECLAIM_CLEAN;
bool dirty, writeback;
cond_resched();
page = lru_to_page(page_list);
list_del(&page->lru);
if (!trylock_page(page))//如果页面被锁住则跳过
goto keep;
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(PageActive(page), page);
sc->nr_scanned++;//增加扫描计数
//如果是page_evictable页,尝试设置activate并放到ret_page中
if (unlikely(!page_evictable(page)))
goto activate_locked;
//如果是映射到进程的页,但不允许回收映射则解锁后放到ret_page中
if (!sc->may_unmap && page_mapped(page))
goto keep_locked;
/* Double the slab pressure for mapped and swapcache pages */
//如果是映射页或者交换缓存的页就Double扫描计数,因为可扫描的页不应该快速结束也扫描,否则会影响系统性能
if ((page_mapped(page) || PageSwapCache(page)) &&
!(PageAnon(page) && !PageSwapBacked(page)))
sc->nr_scanned++;
//标记是否允许文件系统操作
may_enter_fs = (sc->gfp_mask & __GFP_FS) ||
(PageSwapCache(page) && (sc->gfp_mask & __GFP_IO));
/*
* The number of dirty pages determines if a node is marked
* reclaim_congested which affects wait_iff_congested. kswapd
* will stall and start writing pages if the tail of the LRU
* is all dirty unqueued pages.
*/
//判断是否为脏页或者在回写处理中
page_check_dirty_writeback(page, &dirty, &writeback);
if (dirty || writeback)
nr_dirty++;//记录回写脏页数量
if (dirty && !writeback)
nr_unqueued_dirty++;//未回写脏页数量
/*
* Treat this page as congested if the underlying BDI is or if
* pages are cycling through the LRU so quickly that the
* pages marked for immediate reclaim are making it to the
* end of the LRU a second time.
*/
//判断是否映射页,文件页返回MAPPING,匿名页返回NULL,交换缓存页返回SWAP
mapping = page_mapping(page);
//增加阻塞页框的两种情况:1.脏页或者在回写的页的inode标志位阻塞,2.回写的页标记正在回收
if (((dirty || writeback) && mapping &&
inode_write_congested(mapping->host)) ||
(writeback && PageReclaim(page)))
nr_congested++;
/*
* If a page at the tail of the LRU is under writeback, there
* are three cases to consider.
*
* 1) If reclaim is encountering an excessive number of pages
* under writeback and this page is both under writeback and
* PageReclaim then it indicates that pages are being queued
* for IO but are being recycled through the LRU before the
* IO can complete. Waiting on the page itself risks an
* indefinite stall if it is impossible to writeback the
* page due to IO error or disconnected storage so instead
* note that the LRU is being scanned too quickly and the
* caller can stall after page list has been processed.
*
* 2) Global or new memcg reclaim encounters a page that is
* not marked for immediate reclaim, or the caller does not
* have __GFP_FS (or __GFP_IO if its simply going to swap,
* not to fs). In this case mark the page for immediate
* reclaim and continue scanning.
*
* Require may_enter_fs because we would wait on fs, which
* may not have submitted IO yet. And the loop driver might
* enter reclaim, and deadlock if it waits on a page for
* which it is needed to do the write (loop masks off
* __GFP_IO|__GFP_FS for this reason); but more thought
* would probably show more reasons.
*
* 3) Legacy memcg encounters a page that is already marked
* PageReclaim. memcg does not have any dirty pages
* throttling so we could easily OOM just because too many
* pages are in writeback and there is nothing else to
* reclaim. Wait for the writeback to complete.
*
* In cases 1) and 2) we activate the pages to get them out of
* the way while we continue scanning for clean pages on the
* inactive list and refilling from the active list. The
* observation here is that waiting for disk writes is more
* expensive than potentially causing reloads down the line.
* Since theyre marked for immediate reclaim, they wont put
* memory pressure on the cache working set any longer than it
* takes to write them to disk.
*/
//如果页处于回写状态中
if (PageWriteback(page)) {
/* Case 1 above */
//页在交换中
if (current_is_kswapd() &&
PageReclaim(page) &&
test_bit(PGDAT_WRITEBACK, &pgdat->flags)) {
nr_immediate++;
goto activate_locked;
/* Case 2 above */
//页再回收中
} else if (sane_reclaim(sc) ||
!PageReclaim(page) || !may_enter_fs) {
/*
* This is slightly racy - end_page_writeback()
* might have just cleared PageReclaim, then
* setting PageReclaim here end up interpreted
* as PageReadahead - but that does not matter
* enough to care. What we do want is for this
* page to have PageReclaim set next time memcg
* reclaim reaches the tests above, so it will
* then wait_on_page_writeback() to avoid OOM;
* and its also appropriate in global reclaim.
*/
SetPageReclaim(page);
nr_writeback++;
goto activate_locked;
/* Case 3 above */
//不在交换也不在回收,则等待回写完毕
} else {
unlock_page(page);
wait_on_page_writeback(page);
/* then go back and try same page again */
list_add_tail(&page->lru, page_list);
continue;
}
}
if (!force_reclaim)//如果没有设置强制回收则检查也的访问情况
references = page_check_references(page, sc);
switch (references) {
case PAGEREF_ACTIVATE:
goto activate_locked;//近期访问次数大于1则设置为activate,并且放到ret_page中
case PAGEREF_KEEP:
nr_ref_keep++;
goto keep_locked;
case PAGEREF_RECLAIM:
case PAGEREF_RECLAIM_CLEAN:
; /* try to reclaim the page below */
}
/*
* Anonymous process memory has backing store?
* Try to allocate it some swap space here.
* Lazyfree page could be freed directly
*/
//如果是匿名也且有后备缓存
if (PageAnon(page) && PageSwapBacked(page)) {
if (!PageSwapCache(page)) {//不在交换缓存中
if (!(sc->gfp_mask & __GFP_IO))
goto keep_locked;
if (PageTransHuge(page)) {
/* cannot split THP, skip it */
if (!can_split_huge_page(page, NULL))
goto activate_locked;
/*
* Split pages without a PMD map right
* away. Chances are some or all of the
* tail pages can be freed without IO.
*/
if (!compound_mapcount(page) &&
split_huge_page_to_list(page,
page_list))
goto activate_locked;
}
if (!add_to_swap(page)) {
if (!PageTransHuge(page))
goto activate_locked;
/* Fallback to swap normal pages */
if (split_huge_page_to_list(page,
page_list))
goto activate_locked;
#ifdef CONFIG_TRANSPARENT_HUGEPAGE
count_vm_event(THP_SWPOUT_FALLBACK);
#endif
if (!add_to_swap(page))
goto activate_locked;
}
may_enter_fs = 1;
/* Adding to swap updated mapping */
mapping = page_mapping(page);//添加到交换缓存中
}
} else if (unlikely(PageTransHuge(page))) {
/* Split file THP */
if (split_huge_page_to_list(page, page_list))
goto keep_locked;
}
/*
* The page is mapped into the page tables of one or more
* processes. Try to unmap it here.
*/
//如果页有映射到进程
if (page_mapped(page)) {
enum ttu_flags flags = ttu_flags | TTU_BATCH_FLUSH;
if (unlikely(PageTransHuge(page)))
flags |= TTU_SPLIT_HUGE_PMD;
if (!try_to_unmap(page, flags)) {//尝试接触映射
nr_unmap_fail++;
goto activate_locked;
}
}
if (PageDirty(page)) {//如果是脏页
/*
* Only kswapd can writeback filesystem pages
* to avoid risk of stack overflow. But avoid
* injecting inefficient single-page IO into
* flusher writeback as much as possible: only
* write pages when weve encountered many
* dirty pages, and when weve already scanned
* the rest of the LRU for clean pages and see
* the same dirty pages again (PageReclaim).
*/
/* 如果这个是文件页,但是想要往下回收还要满足三个条件:
1.是kswapd线程,只有kswapd可以回写文件系统页面,以避免堆栈溢出的风险
2.是正在回收的页
3.是大量脏页处理的回写操作,只有当我们遇到许多脏页时才写页,避免将低效的单页IO
如果满足三个要求,可以往下走,否则走activate_locked设置为活动页
*/
if (page_is_file_cache(page) &&
(!current_is_kswapd() || !PageReclaim(page) ||
!test_bit(PGDAT_DIRTY, &pgdat->flags))) {
/*
* Immediately reclaim when written back.
* Similar in principal to deactivate_page()
* except we already have the page isolated
* and know its dirty
*/
inc_node_page_state(page, NR_VMSCAN_IMMEDIATE);
SetPageReclaim(page);
goto activate_locked;
}
if (references == PAGEREF_RECLAIM_CLEAN)//如果被访问过就放到ret_page中
goto keep_locked;
if (!may_enter_fs)//不允许文件系统操作就放到ret_page中
goto keep_locked;
if (!sc->may_writepage)//不允许回写则放到ret_page中
goto keep_locked;
/*
* Page is dirty. Flush the TLB if a writable entry
* potentially exists to avoid CPU writes after IO
* starts and then write it out here.
*/
//走到这里说明页面很脏。 如果可能存在可写条目,则刷新TLB,以避免IO启动后进行CPU写操作,然后在这里将其写入。
try_to_unmap_flush_dirty();
switch (pageout(page, mapping, sc)) {//将页面回写出去操作
case PAGE_KEEP:
goto keep_locked;
case PAGE_ACTIVATE:
goto activate_locked;
case PAGE_SUCCESS:
if (PageWriteback(page))
goto keep;
if (PageDirty(page))
goto keep;
/*
* A synchronous write - probably a ramdisk. Go
* ahead and try to reclaim the page.
*/
if (!trylock_page(page))
goto keep;
if (PageDirty(page) || PageWriteback(page))
goto keep_locked;
mapping = page_mapping(page);
case PAGE_CLEAN:
; /* try to free the page below */
}
}
/*
* If the page has buffers, try to free the buffer mappings
* associated with this page. If we succeed we try to free
* the page as well.
*
* We do this even if the page is PageDirty().
* try_to_release_page() does not perform I/O, but it is
* possible for a page to have PageDirty set, but it is actually
* clean (all its buffers are clean). This happens if the
* buffers were written out directly, with submit_bh(). ext3
* will do this, as well as the blockdev mapping.
* try_to_release_page() will discover that cleanness and will
* drop the buffers and mark the page clean - it can be freed.
*
* Rarely, pages can have buffers and no ->mapping. These are
* the pages which were not successfully invalidated in
* truncate_complete_page(). We try to drop those buffers here
* and if that worked, and the page is no longer mapped into
* process address space (page_count == 1) it can be freed.
* Otherwise, leave the page on the LRU so it is swappable.
*/
if (page_has_private(page)) {
if (!try_to_release_page(page, sc->gfp_mask))
goto activate_locked;
if (!mapping && page_count(page) == 1) {
unlock_page(page);
if (put_page_testzero(page))
goto free_it;
else {
/*
* rare race with speculative reference.
* the speculative reference will free
* this page shortly, so we may
* increment nr_reclaimed here (and
* leave it off the LRU).
*/
nr_reclaimed++;
continue;
}
}
}
if (PageAnon(page) && !PageSwapBacked(page)) {
/* follow __remove_mapping for reference */
if (!page_ref_freeze(page, 1))
goto keep_locked;
if (PageDirty(page)) {
page_ref_unfreeze(page, 1);
goto keep_locked;
}
count_vm_event(PGLAZYFREED);
count_memcg_page_event(page, PGLAZYFREED);
} else if (!mapping || !__remove_mapping(mapping, page, true))
goto keep_locked;
/*
* At this point, we have no other references and there is
* no way to pick any more up (removed from LRU, removed
* from pagecache). Can use non-atomic bitops now (and
* we obviously dont have to worry about waking up a process
* waiting on the page lock, because there are no references.
*/
__ClearPageLocked(page);
free_it:
nr_reclaimed++;
/*
* Is there need to periodically free_page_list? It would
* appear not as the counts should be low
*/
if (unlikely(PageTransHuge(page))) {
mem_cgroup_uncharge(page);
(*get_compound_page_dtor(page))(page);
} else
list_add(&page->lru, &free_pages);//将页面放入free_pages释放掉
continue;
activate_locked:
/* Not a candidate for swapping, so reclaim swap space. */
if (PageSwapCache(page) && (mem_cgroup_swap_full(page) ||
PageMlocked(page)))
try_to_free_swap(page);
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(PageActive(page), page);
if (!PageMlocked(page)) {
SetPageActive(page);
pgactivate++;
count_memcg_page_event(page, PGACTIVATE);
}
keep_locked:
unlock_page(page);
keep:
list_add(&page->lru, &ret_pages);
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(PageLRU(page) || PageUnevictable(page), page);
}
mem_cgroup_uncharge_list(&free_pages);
try_to_unmap_flush();
//释放空闲页,没有释放成功则通过free_pages返回
free_unref_page_list(&free_pages);
list_splice(&ret_pages, page_list);
count_vm_events(PGACTIVATE, pgactivate);
if (stat) {
stat->nr_dirty = nr_dirty;
stat->nr_congested = nr_congested;
stat->nr_unqueued_dirty = nr_unqueued_dirty;
stat->nr_writeback = nr_writeback;
stat->nr_immediate = nr_immediate;
stat->nr_activate = pgactivate;
stat->nr_ref_keep = nr_ref_keep;
stat->nr_unmap_fail = nr_unmap_fail;
}
return nr_reclaimed;//返回直接回收的页数量
}1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.46.47.48.49.50.51.52.53.54.55.56.57.58.59.60.61.62.63.64.65.66.67.68.69.70.71.72.73.74.75.76.77.78.79.80.81.82.83.84.85.86.87.88.89.90.91.92.93.94.95.96.97.98.99.100.101.102.103.104.105.106.107.108.109.110.111.112.113.114.115.116.117.118.119.120.121.122.123.124.125.126.127.128.129.130.131.132.133.134.135.136.137.138.139.140.141.142.143.144.145.146.147.148.149.150.151.152.153.154.155.156.157.158.159.160.161.162.163.164.165.166.167.168.169.170.171.172.173.174.175.176.177.178.179.180.181.182.183.184.185.186.187.188.189.190.191.192.193.194.195.196.197.198.199.200.201.202.203.204.205.206.207.208.209.210.211.212.213.214.215.216.217.218.219.220.221.222.223.224.225.226.227.228.229.230.231.232.233.234.235.236.237.238.239.240.241.242.243.244.245.246.247.248.249.250.251.252.253.254.255.256.257.258.259.260.261.262.263.264.265.266.267.268.269.270.271.272.273.274.275.276.277.278.279.280.281.282.283.284.285.286.287.288.289.290.291.292.293.294.295.296.297.298.299.300.301.302.303.304.305.306.307.308.309.310.311.312.313.314.315.316.317.318.319.320.321.322.323.324.325.326.327.328.329.330.331.332.333.334.335.336.337.338.339.340.341.342.343.344.345.346.347.348.349.350.351.352.353.354.355.356.357.358.359.360.361.362.363.364.365.366.367.368.369.370.371.372.373.374.375.376.377.378.379.380.381.382.383.384.385.386.387.388.389.390.391.392.393.394.395.396.397.398.399.400.401.402.403.404.405.406.407.408.409.410.411.412.413.414.415.416.417.418.419.420.421.422.423.424.425.426.427.428.429.430.431.432.433.434.
内存直接回收流程就到此结束了。
四、页面回收的时机与场景
4.1周期性检查与 kswapd 守护进程
kswapd 守护进程,就像是 Linux 系统内存管理中的一位忠实的守护者,默默地在后台运行着 。它的主要职责是定期检查系统的内存使用情况,确保内存资源的合理利用 。就像一位勤劳的管家,会定期检查家里的物品摆放和使用情况,以便及时清理和整理 。
kswapd 守护进程会按照一定的时间间隔,周期性地醒来并检查系统的内存状态 。在检查过程中,它会重点关注系统的空闲内存数量 。当它发现空闲内存低于特定的阈值时,就如同管家发现家里的空间变得拥挤,需要清理出一些空间一样,kswapd 会立即发起页面回收操作 。
在一个运行着多个应用程序的 Linux 服务器上,假设数据库应用占用了大量内存,使得空闲内存逐渐减少 。当空闲内存低于 kswapd 设定的阈值时,kswapd 就会被唤醒并开始工作 。它会仔细遍历内存中的页面,根据之前介绍的 LRU 算法和其他相关机制,将那些最近最少使用的页面标记为可回收页面 。
这些页面可能包括缓存的文件数据,也就是页缓存,就像我们暂时放在家里某个角落的物品;也可能是进程的匿名内存,比如堆和栈,这些就像是我们在使用过程中产生的临时物品 。对于页缓存,由于文件数据可以从磁盘重新读取,kswapd 可以直接释放这些页面,就像把暂时不用的物品直接扔掉;而对于匿名内存,kswapd 可能会将页面内容交换到磁盘上的交换空间,这就好比把暂时不用的物品存放到仓库里,以便为其他进程腾出宝贵的物理内存 。
4.2直接页面回收
在某些特殊情况下,会触发直接页面回收 。当系统需要通过伙伴系统为用户进程分配一大块内存,或者需要创建一个很大的缓冲区时,如果当时系统中的内存无法提供足够多的物理内存来满足这种内存请求,就像一个人在建造大房子时,发现现有的建筑材料不够,这时候就会触发直接页面回收 。在内存分配失败时,系统会立即启动直接页面回收操作,试图从当前已分配的内存中回收一些页面,以满足新的内存需求 。
直接页面回收与 kswapd 回收有着明显的区别 。kswapd 回收是一种周期性的、较为温和的内存回收方式,它就像一个定期打扫房间的管家,按照一定的时间规律来清理内存 。而直接页面回收则是在内存分配面临紧急需求时的一种应急措施,更像是在房子建造过程中材料不足时,立刻从其他地方紧急调配材料 。直接页面回收由内存分配请求的发起者直接触发,并且在回收过程中会阻塞当前的内存分配请求,直到回收操作完成或者确定无法满足内存需求为止 。这就好比建造房子的工人在材料不足时,会暂停建造工作,等待材料调配到位 。而 kswapd 回收是由 kswapd 守护进程独立完成,不会阻塞其他进程的运行 。
直接页面回收对系统性能有着重要的影响 。由于它会阻塞当前的内存分配请求,可能会导致相关进程的运行出现短暂的停顿,就像建造房子的工作因为等待材料而暂时停滞,影响了工程进度 。为了优化直接页面回收,可以采取一些措施 。比如,提前预估内存需求,合理调整内存分配策略,避免频繁出现内存分配失败的情况,就像在建造房子前,提前规划好材料的使用量和调配方案,减少紧急调配的次数 。同时,也可以通过优化内存回收算法,提高回收效率,缩短回收时间,让内存分配请求能够尽快得到满足,就像提高材料调配的效率,让建造工作能够尽快恢复 。
4.3特殊场景下的页面回收
在系统进入 suspend - to - disk 状态时,也就是我们常说的睡眠到磁盘状态,内核必须释放内存 。这就好比一个人在睡觉前,会把房间里暂时不用的东西都清理掉,以便有一个舒适的睡眠环境 。在这个过程中,会触发睡眠回收 。睡眠回收会尽可能地释放内存,将内存中的数据保存到磁盘上,确保系统在进入睡眠状态时占用最少的内存资源 。当系统从睡眠状态唤醒时,再从磁盘中读取数据恢复内存状态 。
而当系统在进行了内存回收操作之后,仍然无法回收到足够多的页面以满足内存要求时,OOM killer(内存不足杀手)就会登场 。OOM killer 就像是一个残酷的裁决者,当内存资源极度匮乏时,它会从系统中挑选一个最合适的进程杀死它,并释放该进程所占用的所有页面 。它在选择要杀死的进程时,会根据每个进程的内存使用情况、优先级等因素进行综合评估 。
通常情况下,它会优先选择占用内存较多且优先级较低的进程,就像在一群人中,优先选择那些占地方又不太重要的人离开 。在一个内存资源有限的嵌入式 Linux 设备上,如果同时运行了多个内存密集型应用,并且内存已经耗尽,OOM Killer 会仔细评估各个进程 。它可能会优先终止一些后台的非关键任务进程,将其占用的内存回收,从而保障系统的基本功能和更重要的进程能够继续运行 。
这些特殊场景下的页面回收都有着各自独特的特点 。睡眠回收主要是为了满足系统进入睡眠状态的内存需求,重点在于将内存数据安全地保存到磁盘并释放内存 。而 OOM killer 则是在内存回收失败后的最后一道防线,以牺牲部分进程为代价来保证系统的整体稳定性 。针对这些特殊场景,我们需要采取相应的应对策略 。
在系统设计和应用开发过程中,要合理规划内存使用,避免出现内存过度占用的情况,减少 OOM killer 被触发的概率 。同时,对于一些关键进程,可以通过设置较低的 OOM 分数等方式,提高其在内存紧张时的生存能力 。在系统进入睡眠状态前,要确保内存数据的完整性和可恢复性,以便在唤醒时能够正常运行 。
五、页面回收技术的应用与实践
5.1系统性能优化
在 Linux 系统中,页面回收技术对系统性能的优化起着至关重要的作用,而合理配置页面回收参数则是实现这一优化的关键手段 。其中,swappiness 参数就是一个非常重要的调控旋钮 。swappiness 的值表示系统将内存页面交换到磁盘交换空间的倾向程度,它的取值范围是 0 - 100 。当 swappiness 的值为 0 时,就像一个非常恋家的人,系统几乎不会主动将内存页面交换到磁盘,而是尽可能地使用物理内存 。这在物理内存充足的情况下是非常理想的,因为磁盘 I/O 的速度远远低于内存访问速度,减少磁盘交换可以大大提高系统的运行效率 。比如,在一台配置较高、内存充足的服务器上运行一些对实时性要求较高的应用程序,如数据库服务器、大型游戏服务器等,将 swappiness 设置为 0 可以避免因页面交换而带来的延迟,保证应用程序的高效稳定运行 。
而当 swappiness 的值为 100 时,系统则会非常积极地将内存页面交换到磁盘,就像一个喜欢清理内存的人,只要内存稍有空闲就会将页面交换出去 。这种设置在内存资源非常紧张的情况下,能在一定程度上维持系统的运行,避免因内存耗尽而导致系统崩溃 。但频繁的磁盘交换会带来巨大的性能开销,因为磁盘 I/O 操作比内存访问要慢得多,这会导致系统的响应速度大幅下降,就像一辆车在崎岖的山路上行驶,速度会变得很慢 。
在实际应用中,我们需要根据系统的实际内存使用情况和业务需求来合理调整 swappiness 的值 。对于大多数桌面系统来说,默认的 swappiness 值(通常为 60)可能是比较合适的,它在保证系统稳定性的同时,也能在一定程度上利用磁盘交换空间来应对内存紧张的情况 。但对于一些对内存性能要求极高的服务器应用,我们可能需要将 swappiness 值降低到一个较低的水平,比如 10 或 20 。在一个内存充足的 Web 服务器上,将 swappiness 设置为 10,服务器可以更好地利用物理内存来缓存网页数据和用户请求,减少磁盘 I/O 操作,从而提高响应速度和并发处理能力 。
我们可以通过修改/etc/sysctl.conf文件来永久调整 swappiness 的值,在文件中添加或修改vm.swappiness = [想要的值]这一行,然后执行sudo sysctl -p使设置生效 。也可以使用命令sudo sysctl vm.swappiness=[想要的值]来临时调整 swappiness 的值 。通过合理配置 swappiness 等页面回收参数,我们能够优化系统内存使用,提高系统的响应速度和稳定性,让 Linux 系统在不同的应用场景下都能发挥出最佳性能 。
5.2故障排查与问题解决
在实际应用中,页面回收技术虽然是保障系统内存稳定的重要机制,但有时也会引发一些问题,需要我们掌握有效的排查方法和解决方案 。
CPU 负载过高是页面回收可能引发的问题之一 。当系统内存紧张,频繁进行页面回收时,kswapd 守护进程或直接页面回收操作会占用大量的 CPU 资源 。这是因为页面回收涉及到复杂的内存扫描、页面置换等操作,这些操作需要 CPU 进行大量的计算和判断 。在一个内存资源有限的服务器上,同时运行了多个内存密集型应用,如大型数据库和数据分析程序,随着内存逐渐被耗尽,系统开始频繁进行页面回收 。kswapd 守护进程为了找到可回收的页面,需要不断地遍历内存中的页面列表,判断页面的使用情况和是否可回收,这就导致 CPU 负载急剧升高 。过高的 CPU 负载会使得其他进程无法及时获得 CPU 资源,从而导致系统整体性能下降,响应变得迟缓 。
当怀疑 CPU 负载过高是由页面回收引起时,我们可以通过一些工具来进行排查 。使用top命令可以实时查看系统中各个进程的资源使用情况,包括 CPU 使用率、内存使用量等 。如果发现 kswapd 进程的 CPU 使用率持续较高,那就很有可能是页面回收导致的 。vmstat命令也能提供有用的信息,它可以显示系统的内存状态、交换活动、CPU 活动等统计信息 。通过观察vmstat输出中的si(从磁盘交换到内存的页面数)和so(从内存交换到磁盘的页面数)这两列,如果发现数值较大,说明系统正在频繁进行页面交换,进而可能导致 CPU 负载过高 。
解决 CPU 负载过高的问题,可以从多个方面入手 。增加物理内存是最直接有效的方法,就像给房子增加更多的空间,这样可以减少页面回收的频率,降低 CPU 的负担 。优化应用程序的内存使用也是关键 。检查应用程序是否存在内存泄漏的问题,及时修复这些问题可以避免内存的不必要浪费 。合理调整页面回收参数,如适当降低 swappiness 的值,可以减少系统对交换空间的依赖,降低页面回收的活跃度,从而减轻 CPU 的压力 。
系统响应变慢也是页面回收可能导致的问题 。除了 CPU 负载过高会间接导致系统响应变慢外,页面回收过程中对内存的锁定和操作也会影响其他进程对内存的访问速度 。当直接页面回收发生时,它会阻塞当前的内存分配请求,直到回收操作完成 。这就好比道路施工,会导致交通堵塞,其他车辆(进程)无法顺利通行 。在一个在线交易系统中,当用户进行下单操作时,如果此时发生直接页面回收,内存分配请求被阻塞,那么用户可能会感觉到页面加载缓慢,甚至出现卡顿现象,严重影响用户体验 。
为了解决系统响应变慢的问题,我们可以先使用strace命令来跟踪进程的系统调用,查看是否存在因页面回收而导致的长时间阻塞 。如果发现是直接页面回收导致的问题,可以尝试优化内存分配策略,提前预估内存需求,避免频繁出现内存分配失败触发直接页面回收 。也可以通过调整内存水位参数,让系统更早地进行页面回收,避免内存过度紧张时才进行紧急回收,从而减少对系统响应的影响 。通过这些排查方法和解决方案,我们能够及时发现并解决页面回收技术在实际应用中可能出现的问题,保障系统的稳定高效运行 。
 图片
图片
 图片
图片 图片
图片 图片
图片